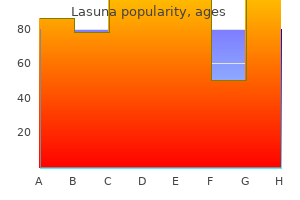
Lasuna
"Discount 60 caps lasuna free shipping, cholesterol levels high during pregnancy".
By: V. Armon, M.A., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Osteopathic Medical College of Wisconsin
T Cell Development and Homeostasis Though supra-pharmacologic doses of glucocorticoids induce T cell apoptosis cholesterol diet vs medication discount 60caps lasuna visa, endogenous glucocorticoid action can induce T cell survival or apoptosis cholesterol medication pfizer buy generic lasuna online, depending on the differentiation stage, the degree of T cell activation and the timing of glucocorticoid exposure (before, during, or after activation). The effect of adrenalectomy in promoting thymocyte expansion in animal models is well known. These and some earlier stages in thymocyte differentiation are exquisitely sensitive to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Indeed, the glucocorticoid-sensitivity of T cell progenitors to the pro-apoptotic effects of glucocorticoids is the reason glucocorticoids are the first line treatment in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and other blood cancers. Concluding Remarks Glucocorticoid effects on the immune response are complex and depend upon many factors: type of glucocorticoid (synthetic or endogenous), cell type, differentiation and activation state, timing of glucocorticoid exposure and the cytokine milieu. Glucocorticoid effects can be immuno-suppressive or stimulatory and even, seemingly, both at the same time. The outcome of glucocorticoid action during an ongoing inflammatory response is different to that when glucocorticoid is administered prior to immune activation. If glucocorticoids are administered during the course of an immune response, they are less effective immunosuppressants than if administered prior to an immune response. Thus, glucocorticoids shape the immune response as it progresses, with different effects during the injury/infection and repair/ resolution/immune memory phases. The great advantage of the clinical use of glucocorticoids in Th1inflammatory and Th1-autoimmune diseases is obvious because they restrain the inflammatory reaction, prevent tissue destruction, and block Th1-driven immune responses. The relative sparing of innate immunity and antibody responses may explain why glucocorticoids exhibit clinical benefit in certain bacterial infections such as in bacterial meningitis. Because of their suppressive actions on Th1 immunity, they increase susceptibility to intracellular and opportunistic infections such as tuberculosis or viral infections. High levels of glucocorticoids may impair early macrophage and neutrophil responses by switching to the resolution phase of inflammation prematurely. The sum total of glucocorticoid action upon a particular immune response is therefore the balance of diverse effects on the many immune cells and inflammatory mediators that comprise a response. A greater understanding of the complexity of these interactions could be useful to enhance ex vivo therapies in auto-immune disease, organ transplants and cancer. Antiinflammatory effects of dexamethasone are partly dependent on induction of dual specificity phosphatase 1. Glucocorticoid therapy of antigen-induced arthritis depends on the dimerized glucocorticoid receptor in T cells. Changing glucocorticoid action: 11b-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in acute and chronic inflammation. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Overview of the actions of glucocorticoids on the immune response: A good model to characterize new pathways of immunosuppression for new treatment strategies. Glucocorticoid hormone-induced chromatin remodeling enhances human hematopoietic stem cell homing and engraftment. Glucocorticoid receptor dimerization is required for survival in septic shock via suppression of interleukin-1 in macrophages. The Th1-Th2 classification of cellular immune responses: Concepts, current thinking and applications in haematological malignancy. Dual specificity phosphatase 1 knockout mice show enhanced susceptibility to anaphylaxis but are sensitive to glucocorticoids. Oxygen levels determine the ability of glucocorticoids to influence neutrophil survival in inflammatory environments. The role of adrenocorticoids as modulators of immune function in health and disease: Neural, endocrine and immune interactions. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: Comparisons and potential for use in the treatment of infections in nonneutropenic patients. Macrophages and neutrophils are the targets for immune suppression by glucocorticoids in contact allergy. Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone and Inflammation Markella Nezi, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Aretaieion Hospital, Athens, Greece Evangelia Zapanti, Alexandra Hospital, Athens, Greece George Mastorakos, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Aretaieion Hospital, Athens, Greece r 2018 Elsevier Inc.
The somatotroph cells are located more laterally and are typically supplied by the long portal veins (Gorczyca and Hardy cholesterol granuloma definition purchase lasuna 60caps amex, 1987) cholesterol test results chart discount lasuna 60 caps line. The blood supply to the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland differs and is supplied by an anastomotic arterial circle derived from the inferior hypophyseal vessels, which arise from the internal carotid artery, as they enter the cavernous sinus. The long hypophyseal vessels and the portal circulation in the stalk are particularly vulnerable to injury from mechanical and shearing forces at the time of brain injury, as they arise in the subarachnoid space and travel through the diaphragm sella. Interruption of this vascular supply will result in anterior lobe infarction with resultant hypopituitarism. This theory is supported by autopsy studies from the 1960s to 1970s which demonstrated tissue necrosis in the anterior pituitary of patients with traumatic brain injury (Daniel et al. Subsequently more recent studies have shown 43% of patients who survive severe traumatic brain injury for longer than 3 h will have pituitary infarction (Salehi et al. Somatotroph and gonadotroph cells lie laterally and are supplied by the long hypophyseal portal vessels, interruption of this blood supply will result in infarction of these cells (Dusick et al. By contrast, the inferior hypophyseal arteries are much less vulnerable to injury and therefore infarction of the posterior pituitary is therefore rare. Secondary insults from hypoxia, hypotension, and cerebral edema frequently complicate major trauma and may contribute to the development of hypopituitarism. In contrast to this, 43% of patients who survived for between 3 h and 1 week after injury had evidence of pituitary infarction (Salehi et al. Harper and colleagues examined pituitary infarcts in 38 of 100 consecutive patients with fatal closed head injuries. Pituitary Disorders Following Traumatic Brain Injury 371 Whilst the exact mechanism remains unclear, it is likely that the pathophysiology is multifaceted and is likely an interplay between mechanical injury to the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, complicated by secondary insults such as hypotension and raised intracranial pressure and the transient stress of critical illness with resultant inflammatory response. Early pituitary dysfunction as a predictor Several studies have evaluated early pituitary dysfunction as a predictor of the development of chronic hypopituitarism. In fact when patients were retested, some patients who had intact pituitary dysfunction earlier had developed new deficiencies (Agha et al. The authors were unable to identify factors predictive of persistent hypopituitarism in this study. In this article, there was no discernible pattern to identify those at higher risk of permanent pituitary deficiencies. Neither of these studies had a control group of critically unwell patients without known pituitary dysfunction. However, when repeat testing was performed 12 months later 6 of 32 patients tested were cortisol deficient, all of whom had acute cortisol deficiency and/or cranial diabetes insipidus in the acute phase. Two separate studies have quantitatively reported the effect of secondary brain injuries (hypoxemia and hypotension) on pituitary function, but neither study demonstrated a predictive association (Krahulik et al. Whilst the optimal timing for screening for pituitary insufficiency is relatively straight forward, establishing which groups to screen-or not to screen-remains challenging. There continues to be much debate as to the ideal approach to screening in traumatic brain injury. Failure to correctly identify and treat affected patients may result in increased morbidity and mortality. The short synacthen test requires time for the adrenal glands to atrophy and is therefore not suitable in the acute setting. In critical illness, the normal diurnal variation of cortisol is typically lost, however a 09. Establishing a safe cut-off value for basal cortisol levels requires a high sensitivity due to the potential repercussions of a missed diagnosis. Other potential causes of polyuria, such as diuretic use, steroid induced hyperglycemia or renal impairment should also be excluded. Chronic hypopituitarism Patient selection Identifying patients that require screening is imperative and is the subject of ongoing debate. In order to determine whether symptom-based screening would improve the diagnostic yield of dynamic testing, we compared the rate of hypopituitarism identified from a referral strategy based only on symptoms suggestive of pituitary dysfunction.
Letrozole reduces estrogen and gonadotropin exposure in women with breast cancer undergoing ovarian stimulation before chemotherapy cholesterol ratio numbers mean order lasuna 60caps overnight delivery. Fertility preservation success subsequent to concurrent aromatase inhibitor treatment and ovarian stimulation in women with breast cancer cholesterol medication for diabetics order 60 caps lasuna with mastercard. Fertility preservation in women with turner syndrome: A comprehensive review and practical guidelines. In vitro fertilization in 37 women with systemic lupus erythematosus or antiphospholipid syndrome: A series of 97 procedures. Current success and efficiency of autologous ovarian transplantation: A meta-analysis. Survival and growth of human preantral follicles after cryopreservation of ovarian tissue, follicle isolation and short-term xenografting. Practice Committees of American Society for Reproductive Medicine, Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology, Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology, 2013. First pregnancy and live birth resulting from cryopreserved embryos obtained from in vitro matured oocytes after oophorectomy in an ovarian cancer patient. Beyond the dichotomy: A tool for distinguishing between experimental, innovative and established treatment. The impact of excision of ovarian endometrioma on ovarian reserve: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ovarian endometrioma ablation using plasma energy versus cystectomy: A step toward better preservation of the ovarian parenchyma in women wishing to conceive. Fresh embryo transfer versus frozen embryo transfer in in vitro fertilization cycles: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Random-start controlled ovarian hyperstimulation for emergency fertility preservation in letrozole cycles. Successful fertility preservation following ovarian tissue vitrification in patients with primary ovarian insufficiency. Ovarian follicle culture: Advances and challenges for human and nonhuman primates. Live birth following in vitro maturation of oocytes retrieved from extracorporeal ovarian tissue aspiration and embryo cryopreservation for 5 years. Ninety-five orthotopic transplantations in 74 women of ovarian tissue after cytotoxic treatment in a fertility preservation network: Tissue activity, pregnancy and delivery rates. How many oocytes are optimal to achieve multiple live births with one stimulation cycle Ovarian stimulation to cryopreserve fertilized oocytes in cancer patients can be started in the luteal phase. Concurrent treatment with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists for chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage in premenopausal women with breast cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Female Hormonal Contraception Genevieve Plu-Bureau, Paris Descartes University, Paris, France r 2019 Elsevier Inc. The use of contraceptive methods aims to prevent the occurrence of an unwanted pregnancy during a given period and this, reversibly. The ideal contraception should be totally effective, acceptable, perfectly well tolerated, while preserving the subsequent fertility (United Nations, 2013). Despite a very wide choice of contraceptive methods currently available, such contraception does not exist. Subsequent developed newer-generation progestins have resulted in a stronger progestogenic activity and decreased androgenic effects such as acne, hirsutism and deleterious lipid changes (Sitruk-Ware and Nath, 2010).
Diseases
- Craniodiaphyseal dysplasia
- Young Mc keever Squier syndrome
- Mediastinal endodermal sinus tumors
- Morse Rawnsley Sargent syndrome
- Enolase deficiency type 2
- Lymphedema, congenital
- Gastroenteritis