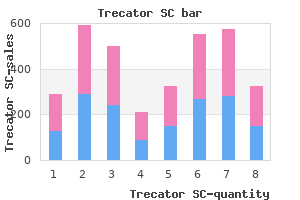
Trecator SC
"250 mg trecator sc fast delivery, medicine etymology".
By: Q. Curtis, M.A., Ph.D.
Professor, Medical University of South Carolina College of Medicine
It is called the "thyroid" cartilage because the thyroid gland is draped over part of it symptoms nervous breakdown purchase cheap trecator sc. The cricoid cartilage is shaped like a signet ring symptoms gallbladder cheap trecator sc 250 mg without prescription, and it completely encircles the top of the trachea, to which it is attached. The broader part of this signet ring forms the lower rear wall of the larynx and the thin part of the cricoid ring is located in front. Supported within these larger cartilages forming the outer walls of the larynx are smaller ones that support the vocal folds, tissues that vibrate to produce sounds as air passes over them. The epiglottis guards the entrance to the larynx from above, protecting it from the things you eat and drink. The "stem" portion is anchored to the anterior rim of the thyroid cartilage and acts like a hinge for this doorway to the airways. The broader (or "leaf") end of the epiglottis is unattached, allowing the epiglottis to swing up and down like a trap door. When we swallow, the larynx moves upward and, at the same time, the epiglottis flaps down to close off the airways below. This movement of the epiglottis helps direct food and drink into the esophagus and keeps them out of our lungs. The ability to speak allows us to communicate and interact with one another in ways that other creatures cannot. When we speak or sing, we force air from our lungs through the glottis and past the true vocal cords. Muscles in the larynx can increase or decrease the tension on the vocal cords, causing a change in the sound. When vocal cords are more relaxed, they vibrate slower, resulting in a lower pitch. Alternatively, when vocal cords are tighter, they vibrate most rapidly, resulting in a higher pitch. This is because due to the effect of androgens (male sex hormones) men have slightly longer and thicker vocal cords. The nasal and oral cavities, as well as the sinuses, contribute to the resonance of our voices. The movement of the tongue, lips, and pharynx help mold sound into recognizable speech. The force with which air is pushed from the lungs past the vocal cords plays a very important role in the loudness of our voice. Inflammation of the vocal cords (vocal folds) can cause swelling and pain, keeping them from moving normally during speech. In severe cases, the swelling can be so extensive as to almost prevent the vocal cords from vibrating. Laryngitis can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, allergies, or inhalation of chemical fumes. Irritation of the larynx can also result from chemical burns caused by stomach acid that sometimes percolates up the esophagus and slips over into the larynx. Normal vocal chords Swollen vocal chords 72 the Trachea the trachea, or windpipe, begins at the larynx and runs down into the chest. The wall of the trachea has four layers: mucosa, submucosa, hyaline cartilage, and adventitia. Like the other airways in the respiratory system, the trachea is much more than a tube. The trachea, as well as most of the airways we are discussing, is lined with a mucous membrane that produces dustcatching mucus and sweeps it away with microscopic cilia. The inner layers of the trachea - the mucosa and and submucosa beneath it - are packed with mucus-producing goblet cells. Cilia - hairlike projections from the ciliated cells - continually move mucus containing dust and debris toward the pharynx. Heimlich Maneuver Occasionally a person may have his or her airway completely blocked by a piece of food. Food Pharynx Trachea In recent years, a procedure known as the Heimlich maneuver was developed to enable laymen with some knowledge of first aid to help in these emergencies, sometimes providing life-saving help long before medical professionals could arrive.
Diseases
- Scleroatonic myopathy
- Hypercalcemia, familial benign
- Filippi syndrome
- Macrocephaly mesomelic arms talipes
- Constitutional growth delay
- Pulmonaryatresia intact ventricular septum
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Brachycephalofrontonasal dysplasia
- Hypomelanotic disorder
Women who drink while pregnant have a chance of having a child affected to some degree by prenatal exposure to alcohol medicine descriptions purchase 250 mg trecator sc with visa. Women who work with textile dyes symptoms uterine fibroids cheap trecator sc 250 mg overnight delivery, lead, certain photographic chemicals, semiconductor materials, mercury, and cadmium have increased rates of spontaneous abortion and delivering children with birth defects. Men whose jobs expose them to sustained heat, such as smelter workers, glass manufacturers, and bakers, may produce sperm that can fertilize a secondary oocyte, but possibly lead to spontaneous abortion or a birth defect. Tubes can be inserted to remove abnormal fluid accumulations, such as in the bladder or in the brain, and tumors removed. Correcting the neural tube defect spina bifida in a fetus is more successful in enabling the child to eventually walk than correcting the defect after birth. Fetal Blood and Circulation Throughout fetal development, the maternal blood supplies oxygen and nutrients and carries away wastes. These substances diffuse between the maternal and fetal blood through the placental membrane, and the umbilical blood vessels carry them to and from the fetus (fig. The fetal blood and cardiovascular system are adapted to this intrauterine environment. For example, the concentration of oxygen-carrying hemoglobin in the fetal blood is about 50% greater than in the maternal blood, and fetal hemoglobin has a greater attraction for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin. As a result of these adaptations, at the oxygen partial pressure of the placental capillaries, fetal hemoglobin can carry 20% to 30% more oxygen than adult hemoglobin. Different genes encode the protein subunits of hemoglobin in embryos, fetuses, and individuals after birth. In the fetal cardiovascular system, the umbilical vein transports blood rich in oxygen and nutrients from the placenta to the fetal body. This vein enters the body through the umbilical ring and continues along the anterior abdominal wall to the liver. About half the blood it carries passes into the liver, and the rest enters a vessel called the ductus venosus (duktus ven-osus), which bypasses the liver. There, oxygen-rich blood from the placenta mixes with oxygen-poor blood from the lower parts of the fetal body. Postnatally, the blood from the right atrium enters the right ventricle and is pumped through the pulmonary trunk and pulmonary arteries to the lungs. In the fetus, however, the lungs are not functioning in gas exchange, and the blood largely bypasses them. As blood from the inferior vena cava enters the fetal right atrium, much of it is shunted directly into the left atrium through an opening in the atrial septum. This opening is called the foramen ovale (fo-ramen o-vale), and the blood passes through it because the blood pressure in the right atrium is greater than that in the left atrium. Furthermore, a small valvelike structure (septum primum) on the left side of the atrial septum overlaps the foramen ovale and helps prevent blood from moving in the reverse direction. The rest of the fetal blood entering the right atrium, including a large proportion of the oxygen-poor blood entering from the superior vena cava, passes into the right ventricle and out through the pulmonary trunk. Only a small volume of blood enters the pulmonary circuit because the lungs are collapsed and their blood vessels have a high resistance to blood flow. Most of the blood in the pulmonary trunk bypasses the lungs by entering a fetal vessel called the ductus arteriosus (duktus ar-tere-osus), which connects the pulmonary trunk to the descending portion of the aortic arch. Uterine wall Umbilical arteries Umbilical vein Fetal capillaries Maternal blood in lacuna Diffusion of oxygen and nutrients into fetal blood Placenta Diffusion of waste substances into maternal blood Chorionic villus Blood flow from fetus, branch of umbilical artery Blood flow to fetus, branch of umbilical vein ing to the heart through the superior vena cava, bypasses the lungs and does not enter the part of the aorta that branches to the heart and brain. Some of it reaches the myocardium through the coronary arteries, and some reaches the brain tissues through the carotid arteries. Blood carried by the descending aorta includes the lessoxygenated blood from the ductus arteriosus. Some of the blood is carried into the branches of the aorta that lead to the lower regions of the body. This condition is often associated with other cardiovascular, urogenital, or gastrointestinal disorders. The vessels in the severed cord are routinely counted following a birth to rule out these conditions. At the time of birth, important adjustments must occur in the cardiovascular system when the placenta ceases to function and the newborn begins to breathe.
Many sperm cells may reach a secondary oocyte medications on carry on luggage buy trecator sc cheap, but usually only one sperm cell fertilizes it (fig medications and mothers milk 2016 buy discount trecator sc 250mg on line. If a second sperm were to enter, the fertilized ovum would have three sets of chromosomes and be very unlikely to develop. A secondary oocyte may survive for only twelve to twentyfour hours following ovulation. An enzyme associated with the sperm cell membrane (hyaluronidase) aids this initial penetration (fig. With this contact, the acrosome releases enzymes by exocytosis that digest the material of the zona pellucida. Hundreds of sperm take part in removing the layers that surround the oocyte, but only one sperm will actually fertilize the oocyte. Then the sperm head enters the secondary oocyte, leaving the mitochondria-rich middle section and tail outside. Sperm entry triggers lysosome-like vesicles just beneath the oocyte cell membrane to release enzymes that harden the zona pellucida. Researchers identified the sperm protein, naming it Izumo1 after a Japanese marriage shrine, in 2005, and the receptor on the oocyte, naming it Juno for the Roman goddess of fertility, in 2014. So far the two proteins that orchestrate conception have been found in several mammalian species. The genes that encode the proteins are in the human genome, so the search is on to observe Izumo1 and Juno as human gametes meet. Applicants must have completed the same prerequisites as medical school requirements, including courses in anatomy and physiology, chemistry, microbiology, and biology. Training includes the prerequisite subjects in greater depth, and adds pathophysiology, biochemistry, psychology, pharmacology, physical diagnosis, clinical laboratory science, and bioethics. A minimum of 2,000 hours of clinical rotations provides experience in pediatrics, family medicine, internal medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, emergency medicine, general surgery, and psychiatry. The approaching nuclei from the two sex cells are called pronuclei, until they join. When the pronuclei unite, their nuclear membranes disassemble, and their chromosomes mingle, nishing the process of fertilization. Each sex cell has 23 chromosomes, so the product of fertilization is a cell with 46 chromosomes-the usual number in a human body cell (somatic cell). Abnormal production of gametes or blockages that impede this meeting of cells can result in infertility (see Clinical Applications 22. The procedures usually involve a laboratory technique and sometimes participation of a third person. For many years, donating sperm was a way for male medical students to earn a few extra dollars. Since 1983 sperm banks have asked donors if they wish to be contacted by their children years later. Today several websites offer DnA tests that help people find their sperm donor fathers. A physician in California used his own sperm for intrauterine insemination of fifteen patients and told them that he had used sperm from anonymous donors. Cases of sperm donors fathering more than 150 children each led to sperm donation limits. A plane crash killed the wealthy parents of two early embryos frozen in a hospital in Melbourne, Australia. A man sued his ex-wife for possession of their frozen embryos as part of the divorce settlement. A couple expecting a child can estimate the approximate time of fertilization (conception) by adding 14 days to the date of the onset of the last menstrual period. They can predict the time of birth by adding 266 days (38 weeks) to the fertilization date.
A sperm cell moves treatment 32 best purchase for trecator sc, by its tail lashing and muscular contraction in the female reproductive tract symptoms 5th week of pregnancy order 250 mg trecator sc otc, into a uterine tube. With the aid of enzymes, a sperm cell penetrates the corona radiata and zona pellucida. Fusion of the pronuclei of a sperm and a secondary oocyte completes fertilization. The prenatal period of the offspring is divided into the embryonic stage and the fetal stage. During cleavage the zygote undergoes mitosis, and the newly formed cells divide mitotically. Extraembryonic membrane formation and placentation (1) the trophoblast and its lining layer of cells form the chorion. Gastrulation and organogenesis (1) Gastrulation is the movement of cells within the embryonic disc to form layers. The body enlarges, upper and lower limbs reach final relative proportions, the skin is covered with sebum and dead epidermal cells, the skeleton continues to ossify, external reproductive organs are distinguishable as male or female, muscles contract, and fat is deposited in subcutaneous tissue. Fetal blood and circulation promote reception of oxygen and nutrients from maternal blood and wastes being carried away by maternal blood. The placenta secretes placental lactogen that stimulates the development of the breasts and mammary glands. During pregnancy, increasing secretion of aldosterone promotes retention of sodium and body fluid, and increasing secretion of parathyroid hormone helps maintain a high concentration of maternal blood calcium. Reflex response to mechanical stimulation of the nipple causes the posterior pituitary gland to release oxytocin, which releases milk from the alveolar ducts. As long as milk is removed from the breasts, more milk is produced; if milk is not removed, production ceases. The newborn must begin to respire, obtain nutrients, excrete wastes, and regulate its body temperature. The liver is immature and unable to supply sufficient glucose, so the newborn depends primarily on stored fat for energy. Homeostatic mechanisms may function imperfectly, and body temperature may be unstable. Rapid growth depends on an adequate intake of proteins, vitamins, and minerals in addition to energy sources. It is a period of rapid growth, development of muscular control, and establishment of bladder and bowel control. Physiological and anatomical changes result in a reproductively functional individual. Females may be taller and stronger than males in early adolescence, but the situation reverses in late adolescence. Adolescents develop high levels of motor skills, their intellectual abilities increase, and they continue to mature emotionally. The adult remains relatively unchanged physiologically and anatomically for many years. Degenerative changes continue, and the body becomes less able to cope with demands. Changes occur because of prolonged use, effects of disease, and cellular alterations. An aging person usually loses some intellectual functions, sensory functions, and physiological coordinating capacities. Death usually results from mechanical disturbances in the cardiovascular system or from disease processes that affect vital organs. The skin becomes mottled as circulation slows and congestion and loud breathing occur. Passive aging entails breakdown of structures and slowing or failure of functions. Why can twins resulting from a single fertilized secondary oocyte exchange blood or receive organ transplants from each other without rejection, while twins resulting from two fertilized secondary oocytes in some cases cannot Why do toxins cause more severe medical problems in a child if exposure was during the first eight weeks of prenatal development rather than during the later weeks What technology would enable a fetus born in the fourth month to survive in a laboratory setting