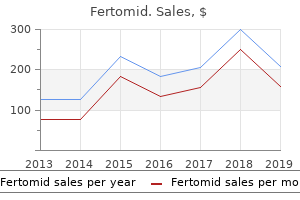
Fertomid
"Purchase cheap fertomid on-line, menstrual hygiene day".
By: N. Tjalf, M.A., M.D.
Associate Professor, New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University
Therefore levels of these glycosides can increase women's health lemon zucchini bars cheap 50 mg fertomid mastercard, thus producing digitalis toxicity menstruation through the ages 50mg fertomid visa. Anyone receiving any of these combinations must be monitored for lower-extremity (especially ankle) and abdominal swelling. Thiazide diuretics may also be used to prevent osteoporosis by increasing calcium reabsorption by the kidneys. Some diuretics remove potassium from the body, causing potentially life-threatening arrhythmias. The primary adverse effects associated with diuretics are fluid and electrolyte imbalances such as muscle weakness and spasm, dizziness, headache, incoordination, and nausea (Box 6. Beta-Blockers Beta-blockers relax the blood vessels and the heart muscle by blocking the beta receptors on the sinoatrial node and myocardial cells, producing a decline in the force of contraction and a reduction in heart rate. This effect eases the strain on the heart by reducing its workload and reducing oxygen consumption. Other potential side effects include depression, worsening of asthma symptoms, sexual dysfunction, and fatigue. Calcium Channel Blockers Calcium channel blockers inhibit calcium from entering the blood vessel walls, where calcium works to constrict blood vessels. Side effects may include swelling in the feet and ankles, orthostatic hypotension, headache, and nausea. Those in the group that primarily interact with calcium channels on the smooth muscle of the peripheral arterioles all end with "pine". This group includes verapamil (Verelan, Calan, Isoptin) and diltiazem (Cardizem, Dilacor). Headache, dizziness, tachycardia, and orthostatic hypotension may occur as a result of the vasodilating properties of these drugs. There are other classes of drugs to treat various aspects of cardiovascular diseases separate from those listed in Table 6. Hyperlipidemia is often treated with medications to inhibit cholesterol synthesis. The therapist should be familiar with the signs or symptoms that require immediate physician referral and those that must be reported to the physician. They can improve cardiac function in individuals with heart failure and are used in persons with diabetes or early kidney damage. Clients often confide in their therapists and describe symptoms of a more serious nature. The physician is able to distinguish among these conditions through a careful history, and medical examination and testing. For example, compared with angina, the pain of true musculoskeletal disorders may last for seconds or hours, is not relieved by nitroglycerin, and may be aggravated by local palpation or by exertion of just the upper body. In the clinical setting, the onset of an anginal attack requires immediate cessation of exercise. Symptoms associated with angina may be reduced immediately, but should subside within 3 to 5 minutes of cessation of activity. If the client is currently taking nitroglycerin, selfadministration of medication is recommended. Relief from anginal pain should occur within 1 to 2 minutes of nitroglycerin administration; some women may obtain similar results with an antacid. If anginal pain is not relieved in 20 minutes or if the client has nausea, vomiting, or profuse sweating, immediate medical intervention may be indicated. Changes in the pattern of angina, such as increased intensity, decreased threshold of stimulus, or longer duration of pain, require immediate intervention by the physician. A client in treatment under these circumstances should either be returned to the care of the nursing staff or, in the case of an outpatient, should be encouraged to contact their physician by telephone for further instruction before leaving the physical therapy department. Women with chest or breast pain who have a positive family history of breast cancer or heart disease should always be referred to a physician for a follow-up examination. Palpitation in any person with a history of unexplained sudden death in the family requires medical evaluation. More than six episodes of palpitations in 1 minute, or palpitations lasting for hours or occurring in association with pain, shortness of breath, fainting, or severe light-headedness require medical evaluation.
Do not poke or mash around to find the pulse; palpation must not provide a massage to the artery because of the risk of liberating a thrombus or plaque menopause knee pain generic 50 mg fertomid with visa, especially in older adults pregnancy 23 weeks discount fertomid 50 mg without prescription. It can be difficult to assess in the obese client; place fingertips of both hands on either side of the pulse site; femoral pulse should be as strong (if not stronger) than radial pulse. Referral for medical evaluation is advised when resting saturation levels fall below 90%. Monitoring the respiratory rate, level of oxygen administered by nasal canula, and SaO2 levels is very important in this client population. Any condition that restricts blood flow (including cold hands) can result in inaccurate SaO2 readings. Relaxation and physiologic quieting techniques can be used to help restore more normal temperatures in the distal extremities. Upright sitting position has been reported to provide the highest oxygen saturation value compared with positioning in supine, prone, or sidelying. Using SaO2 levels may be a good way to document outcomes of positioning programs for clients with impaired ventilation. Other factors affecting pulse oximeter readings can include nail polish and nail coverings, irregular heart rhythms, intravascular dyes, electrical interference, and significant venous pulsation. If the client cannot talk easily, whether at rest or during exercise, SaO2 levels are likely to be inadequate. The measurement (in mm Hg) is listed as: systolic (contraction phase) / diastolic (relaxation phase). Cuff size is important and requires the bladder width-tolength to be at least 1:2. The client should be seated comfortably in a chair with the back and arm supported, legs uncrossed, feet on the floor, and not talking. Inflate the cuff until you no longer hear a pulse sound and then inflate 30 mm more; this is the point of reference for auscultation. Slowly release the valve on the bulb (deflate at a rate of 2 to 3 mm Hg/second) as you listen for the first Korotkoff sound (two consecutive beats signals the systolic reading) and the last Korotkoff sound (diastolic reading). Record date, time of day, client position, extremity measured (arm or leg, left or right), and results for each reading. As soon as the blood begins to flow through the artery again, Korotkoff sounds are heard. The first phase of sound may be followed by a momentary disappearance of sounds that can last from 30 to 40 mm Hg as the needle descends. Following this temporary absence of sound, there are murmuring or swishing sounds (second Korotkoff sound). During phase 4, the sounds become muffled rather abruptly and then are followed by silence, which represents phase 5. From American Heart Association Updates Recommendations for Blood Pressure Measurements in Humans and Experimental Animals, Part 1. If both measurements are within 5 mm Hg of each other, record this as the resting (baseline) measurement. Older models with tubing long enough to put the earpieces in your ears and still place the bell in a laboratory coat pocket should be replaced. The preferred position is seated with the arms parallel and extended in a forward direction (if supine, then parallel to the body). A widened resting pulse pressure often results from stiffening of the aorta secondary to atherosclerosis. Resting pulse pressure consistently greater than 60 to 80 mm Hg is a yellow (caution) flag and is a risk factor for new onset of atrial fibrillation. A high pulse pressure accompanied by bradycardia is a sign of increased intracranial pressure and requires immediate medical evaluation. In a healthy adult, pulse pressure will return to normal within 3 to 10 minutes following moderate exercise. The key is to watch for pulse pressures that are not accommodating during exercise.
Weakness-cogwheeling or giving way of many muscle groups that cannot be explained on a neurologic basis women's health clinic blacktown order genuine fertomid on-line. Sensory disturbance-diminished sensation fitting a "stocking" rather than a dermatomal pattern breast cancer in young women order 50 mg fertomid amex. Disproportionate verbalization, facial expression, muscle tension, and tremor, collapsing, or sweating. Client may exhibit any of the following behaviors during the physical examination: guarding, bracing, rubbing, sighing, clenching teeth, or grimacing. Whole leg pain from the groin down to below the knee in a stocking pattern (not dermatomal or sclerotomal, intermittent) 3. Whole leg giving way or collapsing (intermittent, client maintains upright position) 5. Unable to tolerate any treatment, reaction or side effects to every intervention 7. Emergency admission to hospital for back pain without precipitating traumatic event Simulation tests Distraction tests Regional disturbances Overreaction Adapted from Karas R, McIntosh G, Hall H, et al. The conversion may provide a solution to the conflict or a way to express "forbidden" feelings. It may be a means of enacting the sick role to avoid responsibilities, or it may be a reflection of behaviors learned in childhood. Presentation always includes a motor and/or sensory component that cannot be explained by a known medical or neuromusculoskeletal condition. The clinical presentation is often mistaken for an organic disorder such as multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, or idiopathic dystonias. During manual muscle testing, true weakness results in smooth "giving way" of a muscle group; in hysterical weakness the muscle "breaks" in a series of jerks. Often the results of muscle testing are not consistent with functional abilities observed. For example, the person cannot raise the arm overhead during testing but has no difficulty dressing, or the lower extremity appears flaccid during recumbency but the person can walk on their heels and toes when standing. The physical therapist should carefully evaluate and document all sensory and motor changes. Conversion symptoms are less likely to follow any dermatome, myotome, or sclerotome patterns. The client may be aware of the symptoms but does not know that these problems can be caused by depression, anxiety, or panic disorder. Medical treatment for physiopsychologic disorders can and should be augmented with exercise. Physical activity and exercise has a known benefit in the management of mild-tomoderate psychologic disorders, especially depression and anxiety. Aerobic exercise or strength training have both been shown to be effective in moderating the symptoms of these conditions. The therapist must develop personal coping mechanisms when working with clients who have chronic illnesses or psychologic disturbances. Recognizing clients whose symptoms are the direct result of organic dysfunction helps us in coping with clients who are hostile, ungrateful, noncompliant, negative, or adversarial. Whenever possible, involve a psychiatrist, psychologist, or counselor as a part of the management team. This red flag requires immediate medical referral in the presence of a personal history of cancer of any kind. Data from Davidson J, Dreher H: the anxiety book: developing strength in the face of fear, New York, 2003, Penguin Putnam. We must keep in mind that pain from a disease process or viscerogenic source is often a late symptom rather than a reliable danger signal. For this reason the therapist must remain alert to other signs and symptoms that may be present but unaccounted for. In this chapter, possible pain types associated with viscerogenic conditions have been presented along with three mechanisms by which viscera refer pain to the body (soma). Characteristics of systemic pain compared with musculoskeletal pain are presented, including a closer look at joint pain.
This may seem self-evident but we have observed a wide range of responses when supervising others that supports the need to provide specific guidelines as stated here menopause question and answers cheap fertomid 50 mg without prescription. Additionally womens health magazine recipes purchase fertomid 50 mg with mastercard, groin pain associated with spinal cord tumor is disproportionate to that normally expected with disk disease. Age is an important factor: Teenagers with symptoms of disk herniation should be examined closely for tumor. With the exception of myeloma and rare lymphoma, metastasis to the synovium is unusual. Although any tumor of the bone may appear at the hip, some benign and malignant neoplasms have a propensity to occur at this location. Bone Tumors Osteoid osteoma, a small, benign but painful tumor, is relatively common, with 20% of lesions occurring in the proximal femur and 10% in the pelvis. Males are more commonly affected with a reported range of 67% to 80% of males being under the age of 25 years. Usually, an antalgic gait is present, along with point tenderness over the lesion with restriction of hip motion. A great many varieties of benign and malignant tumors may appear differently, depending on the age of the client and the site and duration of the lesion (Case Example 16. As a dentist, he was often leaning to the left, putting pressure on the left ischium. He was given a steroid injection and was placed on an antiinflammatory (Celebrex) before he went to physical therapy. The client reported a mild loss of hip motion, especially of hip flexion, but no other symptoms of any kind. No significant past medical history and no history of tobacco use were reported; only an occasional beer in social situations was described. The client described himself as being "in good shape" and working out at the local gym four to five times per week. Intervention/Follow-Up: Physical therapy intervention included deep friction massage, iontophoresis, and stretching. Symptoms did not improve after 10 treatment sessions over the next 6 to 8 weeks; in fact, the pain became worse and was now described as "burning. The physical therapist palpated a lump over the ischial tuberosity, described as "swelling"; this was the only new physical finding since his previous visits with the first physical therapist. The client reported increased painful symptoms, including pain at work and at night. No position was comfortable; even lying down without pressure on the buttocks was painful. Result: the orthopedic surgeon did a bursectomy and the pathology report came back with a diagnosis of epithelioid sarcoma. A second surgery was required because the first excision did not have clear margins. The latter two signs may not be obvious when the inflamed bursa is located deep beneath soft tissues or muscles, as in this case. In this case symptoms progressed and did not fit the typical pattern for bursitis. A positive sign may be an indication of abscess, fracture, neoplasm, septic bursitis, or osteomyelitis. Limited straight leg raise with no further hip flexion after bending the knee is a typical positive buttock sign seen with ischial bursitis. The absence of this sign would raise clinical suspicion that the diagnosis of bursitis was not accurate. These pain patterns represent the pathway that genitals take as they migrate during fetal development from their original position, where the kidneys are located in the adult, down the pathways of the ureters to their final location.