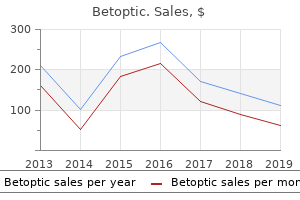
Betoptic
"Cheap betoptic online visa, symptoms 9 days after iui".
By: N. Cronos, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine
Ultrasonography appearance of hematoma depends on multiple factors symptoms neuropathy buy betoptic 5 ml lowest price, especially on its duration symptoms irritable bowel syndrome order 5ml betoptic fast delivery. The early hematoma is echogenic but gradually progresses to sonolucency over 96 hours. Ultrasound has certain limitations as the technique is operator dependent and may be limited by excessive bowel gas (especially in post-traumatic paralytic ileus). In certain circumstances, radionuclide angiography can demonstrate small vascular injuries and may exceed the sensitivity of conventional angiography. Magnetic resonance imaging is useful only in doubtful cases and in hemodynamically stable patients. Angiography With recent trends towards nonoperative management of abdominal trauma patients, angiography with embolization has been increasingly used in the management. Radionuclide Scanning Nuclear medicine studies are generally not used in the screening evaluation of abdominal trauma. It is useful in detecting otherwise occult injuries to both intra-abdominal and retroperitoneal structures and grading severity of specific parenchymal injury. Scans should be done expeditiously and care should be taken to avoid artifacts and repeat scanning. Administration of intravenous iodinated contrast material is mandatory as it makes detection and location of parenchymal contusions and hematoma more conspicuous, identifies great vessels and provides information regarding integrity of organs or extent of the injury. Successful breath holding is often not possible and image acquisition during shallow and quiet breathing is often necessary. It is helpful in defining pancreas, integrity of bowel and free intraperitoneal fluid from fluid filled bowel. It is given orally or through the nasogastric tube and allowed to travel as far as possible through the gastrointestinal tract. Rectal contrast is used occasionally to detect colorectal injuries in patients with perineal lacerations and penetrating flank or back wounds. Delayed scanning of kidneys during urographic phase is essential to detect collecting system injuries. Delayed imaging is also useful in specific situations for differentiating between active contrast extravasation from vascular injuries. When source of intraperitoneal bleed is not evident, the location of highest attenuating blood clot is a clue to the most likely source. Water density fluid collection: Fluid collections of near water attenuation originate from rupture of gallbladder, urinary bladder, small bowel and cisterna chyli. When fluid of this density is encountered in the peritoneal cavity without an identifiable source, the safest assumption is that bowel injury is present. Hemoperitoneum from liver or spleen injury typically does not form such collections, but instead tracks from the upper abdomen along the paracolic gutters into the pelvis. Active arterial contrast extravasation: It must be actively looked for as most oftenly it is an indicator for surgical/ angiographic intervention. It must be distinguished from extravasated oral contrast material and from a vascular injury (pseudoaneurysm or arteriovenous fistula) within an injured organ. Vascular extravasation is typically poorly marginated, high attenuating collection, surrounded by a large hematoma. Vascular injuries show attenuation values paralleling the attenuation of adjacent vessel on delayed phase images while active bleeding shows attenuation values either increasing or remaining same. Computed tomography is required to evaluate the extent of injury and to exclude other intra and retroperitoneal injuries to determine the manage ment approach. It is generally based on the premise that large and deep lacerations, large hematomas and devitalized tissues are signs of more severe injuries and are more likely to require surgical management. Nonoperative management is generally not appropriate in presence of active arterial hemorrhage, favoring urgent surgery or angiographic embolization. Bubbles of free air may be trapped between the leaves of the mesentery or in the peritoneal recesses. Hemoperitoneum Blood collects in the peritoneum following injury to the liver, spleen, bowel or mesentery. Computed tomography is sensitive in detecting intra-abdominal or pelvic hemorrhage.
Postprocedure Care Nowadays the procedure is routinely being done on outpatient basis symptoms 6 weeks discount 5 ml betoptic visa, with a 2 hours observation period after vertebroplasty treatment ringworm purchase betoptic on line amex. Focal pain at the puncture sites may last 2 for days which usually responds to analgesics. Complications Complication rate of vertebroplasty procedure ranges from 1% to 10% with higher rates being reported in the treatment of neoplastic collapse than the osteoporotic collapse. There have been concerns that vertebroplasty may increase the risk of fracture at an adjacent level. Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis: technical report series 843. Official positions of the (International Society for Clinical Densitometry: updated 2005). Establishment of agespecified bone mineral density reference range for Indian females using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Need for measurement of bone mineral density in patients of prostate cancer before and after orchidectomy: role of quantitative computer tomography. Correlation between biochemical bone markers and bone mineral density in the evaluation of osteoporosis. Bone mineral density in childhood survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated without cranial irradiation. Dual X-ray absorptiometry of hip, heel ultrasound, and densitometry of fingers can discriminate male patients with hip fracture from control subjects: a comparison of four different methods. The combined use of ultrasound and densitometry on the prediction of vertebral fractures. Feasibility of in vivo structural analysis of high-resolution magnetic resonance images of the proximal femur. Assessment of trabecular bone structure comparing magnetic resonance imaging at 3 Tesla with high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography ex vivo and in vivo. Imaging of the musculoskeletal system in vivo using ultra-high field magnetic resonance at 7 T. Structural and functional assessment of trabecular and cortical bone by micro magnetic resonance imaging. Geodesic topological analysis of trabecular bone microarchitecture from high-spatial resolution magnetic resonance images. Assessment of Cortical Bone Structure Using High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Proceedings 13th Scientific Meeting, International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine; Miami. In vivo evaluation of the presence of bone marrow in cortical porosity in postmenopausal osteopenic women. Digital topological analysis of in vivo magnetic resonance microimages of trabecular bone reveals structural implications of osteoporosis. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: longterm evaluation of the technical and clinical outcomes. Percutaneous vertebroplasty does not increase the risk of adjacent vertebral fracture-a retrospective study. Benign bone tumors can be classified according to their matrix production and/or predominant cell type into cartilage forming, bone-forming, fibrous, vascular and other connective tissue lesions. For diagnosis of bone tumors and tumor-like lesion, there is need for close cooperation of radiologist, orthopedician and pathologists; however, the role of radiologist is most important. The primary aim of imaging should be to make specific diagnosis (if possible) or narrowing of the differential diagnosis which can be a guide for further intervention and management.
However medicine 5113 v purchase betoptic no prescription, the detection of an adrenal mass in a patient with known malignancy does not necessarily indicate metastatic disease and it may be a nonfunctional adenoma treatment 3 degree heart block discount betoptic 5ml with mastercard. Gradient echo T1W in-phase image (A) shows a hypointense nodule in right adrenal (arrow) which shows marked signal loss on the opposed phase image (B). On the other hand, metastases have little intracytoplasmic fat and thus do not show low attenuation. A large region of interest covering the adrenal mass should be used but should not include periadrenal fat for measuring attenuation value. Although 70% of adenomas have abundant lipid, the remaining are lipid poor and are difficult to characterize on a noncontrast scan. Metastasis also enhance rapidly but the washout is delayed when compared to adenoma. The patient is first scanned without contrast, then again at Chapter 112 Imaging the Adrenal Gland 1787 70 seconds, and then 15 minutes after contrast administration. This technique has a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 96% for the diagnosis of adenoma. It has been said that the relative washout percentage is more accurate for the differentiation of lipid poor adenomas from metastases than are the absolute attenuation values on delayed contrast enhanced scans. This technique is based on the different resonance frequency rates of protons in fat and water molecules in a magnetic field. Thus, adenoma appears darker on out of phase image than on in-phase image, while metastasis will show no significant signal loss on out of phase image and the signal intensity remains unchanged. The liver should not be used as the internal reference as it may also show signal loss on opposed phase image when there is steatosis. Malignant tumors have an increased cellularity which manifests as restricted diffusion, and a decrease in the apparent diffusion coefficient. There are no major published studies specifically on the adrenal, but extrapolating from data on liver, kidney, etc. Adrenal Collision Tumor this is a very rare entity characterized by coexistence of two contiguous but histologically different tumors. Both tumors may be malignant or one may be benign, other malignant or both may be benign. This entity should be suspected when only focal decrease in signal intensity of a mass is seen on opposed phase images or a focus of bright enhancement is seen within a mass which otherwise looks like an adenoma. They are derived from endothelium in 45% of patients and the rest are epithelial, parasitic or pseudocysts from prior hemorrhage. Differential diagnosis includes adenoma, metastases, lymphoma, exophytic liver tumors, or upper polar renal masses. Myelolipoma is a benign tumor of the cortex, comprised of mature fat and hematopoietic elements. Imaging appearance may vary depen ding on which histological component is dominant. Ultrasonography shows well-defined echogenic or heterogeneous adrenal mass, which may be associated with apparent posterior displacement of the diaphragm due to propagation speed artifact resulting from slow speed of sound through the fat. Differential diagnosis includes adrenal adenoma, and large myelolipomas may mimic retroperitoneal lipoma or liposarcoma. Adrenal Lymphoma Primary lymphoma of the adrenal gland is unusual, but its involvement in disseminated lymphoma is common. The presence of skeletal metastasis in association with an adrenal mass in a child strongly suggests the diagnosis of neuroblastoma. Based on size criteria and tumor morphology, it is not always possible to suggest benignity or malignancy. All attempts should be made to characterize an incidental adrenal mass as adenoma or metastasis in a patient with known malignancy. Most neuroblastomas arise from adrenal medulla but may also arise from sympathetic chain, posterior mediastinum being the second most common site.
A hydrophilic guidewire is then used to probe the tract which usually finds its way into the collecting system treatment for hemorrhoids order cheap betoptic on line. Overall symptoms xeroderma pigmentosum purchase betoptic cheap, when major and minor compli cations are considered together, the complication rate is between 10% and 15%. It is often much easier to negotiate areas of narrowing, fistulae or discontinuity in the ureter in an antegrade rather than retrograde manner. Negotiation of an obstructed segment is often facilitated by the use of curved angiographic catheters and hydro philic guidewires. Determination of the correct length of the ureteric stent required can be done by using the bent guidewire technique. The percutaneous external urinary catheter is left in place for 24 hours after the procedure, after which it is capped. Thereafter, if there is no hydronephrosis on sonography and contrast injection shows free flow down the double J stent, the external catheter is removed. Balloon dilatation of benign ureteric strictures may provide durable relief in up to 50% of cases. One should ensure that a solid portion of the tube traverses the site of leak with side-holes above and below. Severe bleeding developing several days after catheter insertion requires further evaluation. A track fistulogram can be obtained by exchanging the nephrostomy catheter with an introducer sheath over a stiff guidewire. Angiographic evaluation for identification of a renal arteriovenous fistula, pseudoaneurysm or vessel laceration should be scheduled without delay in patients with persistent or severe bleeding. Most of these vascular injuries can be managed by the endovascular route, surgical intervention is rarely necessary. A retrorenal colon, an uncommon anatomic variant may be transgressed leading to a nephrocolic fistula. Treat ment is conservative and consists of ensuring adequate urinary drainage by placement of an antegrade or retrograde ureteric stent, and withdrawing the nephrostomy catheter into the colon to allow the nephrocolic track to heal. Replacement of a dislodged catheter is usually possible through the previous tract. The ureteric stent is then placed over the stiff guidewire catheter may not provide adequate urinary diversion. They are usually silent, but large, infected or hemorrhagic cysts can cause symptoms. Large cysts can also cause obstruction of the pelvicalyceal system, pressure atrophy of the adjacent parenchyma and stone formation in obstructed calyces. Various agents which have been used to induce sclerosis of the epithelial lining of the cyst include hypertonic dextrose, hypertonic water-soluble contrast, iophan dylate, absolute alcohol, tetracycline and sodium tetradecyl sulfate. The technique consists of puncture of the cyst under sonographic guidance and aspiration of the cyst contents. Contrast is then injected to demonstrate the internal appearance of the cyst and to rule out any communication of the cyst with the collecting system. If no communication is demonstrated and the cyst is small, sclerosant can be injected amounting to about one-third of the aspirated contents of the cyst.