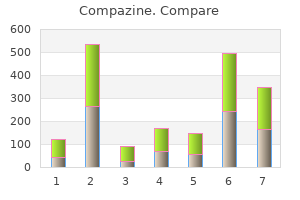
Compazine
"Purchase genuine compazine on-line, treatment 002".
By: K. Mine-Boss, M.A., Ph.D.
Co-Director, New York University School of Medicine
These carcinomas account for 75% of all lung carcinomas treatment 3rd nerve palsy buy generic compazine 5mg on-line, 12% of all malignant tumors symptoms 1974 cheap 5 mg compazine free shipping, and 20% of all cancer deaths in the United States. The combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is the current treatment of choice for small cell carcinomas of the lung. Squamous cell cancers in the superior pulmonary sulcus produce Horner syndrome, as well as characteristic pain in areas served by the eighth cervical nerves and first and second thoracic nerves. These tumors are now treated with preoperative radiation; surgical resection leads to an almost 30% "cure" rate. Some investigators recommend using inhaled bronchodilators as first-line drugs and reducing the dose of inhaled steroids, such as beclomethasone dipropionate, budesonide, mometasone, and fluticasone, which are inactivated after absorption. However, in large doses, these "inhaled" steroids can suppress adrenal function, and supplemental systemic corticosteroids may be needed at times of stress (see the earlier discussion in the section on adrenocortical malfunction). Preoperative assessment must include gaining knowledge of drug regimens and their effects and education of the patient regarding proper use of an inhaler (Box 39-4), given that these drugs can interact dangerously with anesthetics (see the last section of this chapter) or can be used inappropriately and therefore produce side effects without maximum benefit. Allergic applies to immunologically mediated reactions, as opposed to those caused by pharmacologic idiosyncrasy, by direct toxicity or drug overdosage, or by drug interaction. These mediators in turn produce specific end-organ responses in the skin (urticaria), the respiratory system (bronchospasm and upper airway edema), and the cardiovascular system (vasodilation, changes in inotropy, and increased capillary permeability). Vasodilation occurs at the level of the capillary and postcapillary venule and leads to erythema, edema, and smooth muscle contraction. By contrast, an anaphylactoid reaction denotes an identical or very similar clinical response that is not mediated by IgE or (usually) an antigen-antibody process. Low-molecularweight agents are believed to act as haptens that form Chapter 39: Anesthetic Implications of Concurrent Diseases 1195 immunologic conjugates with host proteins. When an allergen binds immunospecific IgE antibodies on the surface of mast cells and basophils, histamine and eosinophilic chemotactic factors of anaphylaxis are released from storage granules in a calcium- and energy-dependent process. These mediators include the following: slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis, which is a combination of three leukotrienes; other leukotrienes255,256; kinins; platelet-activating factors; adenosine; chemotactic factors; heparin; tryptase; chymase; and prostaglandins, including the potent bronchoconstrictor prostaglandin D2; eosinophil growth and activating factors; mast cell growth factors; and proinflammatory and other factors that contribute to the IgE isotype switch. The end-organ effects of the mediators produce the clinical syndrome of anaphylaxis. Usually, a first wave of symptoms, including those caused by vasodilation and a feeling of impending doom, is quickly followed by a second wave as the cascade of mediators amplifies the reactions. In a sensitized patient, onset of the signs and symptoms caused by these mediators is usually immediate but may be delayed 2 to 15 minutes or, in rare instances, as long as 2. Mast cell proliferation, together with severe progressive inflammation, contributes to the worsening of symptoms that occurs even after an allergen load is no longer present. The antigen present in cells and lymphocytes, as well as activated mast cells, starts to induce the production of cytokines. These proinflammatory cytokines recruit more inflammatory cells, a process that leads to tissue edema and mediates a second wave of mast cell degranulation. In addition, biologically active mediators can be generated by multiple effector processes to produce an anaphylactoid reaction. Activation of the blood coagulation and fibrinolytic systems, the kinin-generating sequence, or the complement cascade can produce the same inflammatory substances that result in an anaphylactic reaction. The two mechanisms known to activate the complement system are called classical and alternative. The classical pathway can be initiated through IgG or IgM (transfusion reactions) or plasmin. The alternative pathway can be activated by lipopolysaccharides (endotoxin), drugs (Althesin), radiographic contrast media,259 membranes (nylon tricot membranes for bubble oxygenators), cellophane membranes of dialyzers, vascular graft material,260 latex or latex-containing products,261,262 and perfluorocarbon artificial blood. The most common drugs responsible for intraoperative anaphylaxis are muscle relaxants (see also Chapters 34 and 35). However, latex accounts for a significant number of these reactions, and the incidence of intraoperative anaphylaxis caused by latex is increasing.
Dobrydnjov I treatment 3rd degree burns discount 5 mg compazine overnight delivery, Axelsson K medications used to treat bipolar disorder buy compazine 5mg with amex, Gupta A, et al: Improved analgesia with clonidine when added to local anesthetic during combined spinal-epidural anesthesia for hip arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled study, Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 49(4):538-545, 2005. Burstal R, Wegener F, Hayes C, Lantry G: Subcutaneous tunnelling of epidural catheters for postoperative analgesia to prevent accidental dislodgement: a randomized controlled trial, Anaesth Intensive Care 26(2):147-151, 1998. Curelaru I: Long duration subarachnoid anaesthesia with continuous epidural block, Prakt Anaesth 14(1):71-78, 1979. Brownridge P: Epidural and subarachnoid analgesia for elective caesarean section, Anaesthesia 36(1):70, 1981. Lew E, Yeo S-W, Thomas E: Combined spinal-epidural anesthesia using epidural volume extension leads to faster motor recovery after elective cesarean delivery: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study, Anesth Analg 98(3):810-814, 2004. Lyons G, Macdonald R, Mikl B: Combined epidural/spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section. Major complications of central neuraxial block: report on the Third National Audit Project of the Royal College of Anaesthetists, Br J Anaesth 102(2):179-190, 2009. Reynolds F: Logic in the safe practice of spinal anaesthesia, Anaesthesia 55(11):1045-1046, 2000. Katz N, Hurley R: Epidural anesthesia complicated by fluid collection within the spinal cord, Anesth Analg 77(5):1064-1065, 1993. Takii Y, Sunouchi K, Tadokoro M, et al: Paraplegia from spinal cord injury after thoracic epidural catheterization performed under general anesthesia, Anesth Analg 103(2):513, 2006. Kasai T, Yaegashi K, Hirose M, Tanaka Y: Spinal cord injury in a child caused by an accidental dural puncture with a single-shot thoracic epidural needle, Anesth Analg 96(1):65-67, 2003. Diagnosis, prognosis and prevention of spinal hematoma, Can J Anaesth 51(6):527-534, 2004. Auroy Y, Narchi P, Messiah A, et al: Serious complications related to regional anesthesia: results of a prospective survey in France, Anesthesiology 87(3):479-486, 1997. Incidence and analysis of minor sensory neurological defects, Surgery 38(3):463-469, 1955. Tarkkila P, Huhtala J, Tuominen M: Transient radicular irritation after spinal anaesthesia with hyperbaric 5% lignocaine, Br J Anaesth 74(3):328-329, 1995. Gozdemir M, Muslu B, Sert H, et al: Transient neurological symptoms after spinal anaesthesia with levobupivacaine 5 mg/ml or lidocaine 20 mg/ml, Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 54(1):59-64, 2010. Evron S, Gurstieva V, Ezri T, et al: Transient neurological symptoms after isobaric subarachnoid anesthesia with 2% lidocaine: the impact of needle type, Anesth Analg 105(5):1494-1499, 2007. Hartmann B, Junger A, Klasen J, et al: the incidence and risk factors for hypotension after spinal anesthesia induction: an analysis with automated data collection, Anesth Analg 94(6):1521-1529, 2002. Loubert C: Fluid and vasopressor management for Cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia: continuing professional development, Can J Anaesth 59(6):604-619, 2012. Reynolds F: Damage to the conus medullaris following spinal anaesthesia, Anaesthesia 56(3):238-247, 2001. Denny N, Masters R, Pearson D, et al: Postdural puncture headache after continuous spinal anesthesia, Anesth Analg 66(8):791-794, 1987. The volume of blood for epidural blood patch in obstetrics: a randomized, blinded clinical trial, Anesth Analg 113(1):126-133, 2011. Horn M, Johnson P, Mulroy M: Blood pressure response to an epinephrine test dose in beta-blocked subjects, Anesthesiology 67(3):A268, 1987. Blomberg R: the dorsomedian connective tissue band in the lumbar epidural space of humans: an anatomical study using epiduroscopy in autopsy cases, Anesth Analg 65(7):747-752, 1986.
B symptoms 6 year molars buy compazine canada, Subvolumes are created from a two-dimensional image by dividing up the image into seven subvolumes (white lines) to create a full-volume 3-D image medicine you cannot take with grapefruit purchase compazine 5mg free shipping. Echocardiographers are not limited to 2-D images that may not capture an entire structure of interest at an angle best suited to interrogate it fully. Three-dimensional images also provide a means to work through the image in a sliced bread fashion. When transitioning from 2-D to 3-D imaging, echocardiographers must conceptually move from considering the heart in various slices to a 3-D organ, much the way a surgeon does. With 2-D, a grey scale is used to represent the amplitude of a reflected ultrasound wave from a portion of a scan line and assigned to a corresponding small space on a projected image called a pixel. A similar process is used to assign small volumes according to a grey scale called a voxel. Absolute contraindications include prior esophagectomy, severe esophageal obstruction, esophageal perforation, and ongoing esophageal hemorrhage. Echocardiographers can cut out superficial structures to visualize internal ones by using a cropping tool. For example, to visualize the intraatrial septum in three dimensions, the lateral atrial walls are cropped out. Chapter 46: Perioperative Echocardiography 1411 distal to the endotracheal tube or compress the descending aorta37 (also see Chapter 94). Once the patient is anesthetized and the trachea securely intubated, the contents of the stomach should be removed by gentle suctioning. Gentle massage of the left upper quadrant of the abdomen during suctioning may help remove air that can otherwise degrade imaging. Usually, with minimal force, the probe will blindly pass into the esophagus, especially if the neck is extended. If the probe does not blindly pass, then a laryngoscope is used to lift the larynx anteriorly and the probe is placed into the esophagus under direct vision. During transducer insertion or withdrawal, the controls of the gastroscope must be in the neutral or relaxed position to allow the transducer to follow the natural course of the esophagus, thereby potentially minimizing the risk of injury. Four of the cross sections are imaged in both 2-D and color Doppler imaging to assess valvular function. The next paragraph describes the probe manipulations required to achieve these cross sections. This cross section is best for the detection of ascending aortic abnormalities including type I aortic dissection. For the detection of valvular stenosis and regurgitation, the Nyquist limit is set to 50 to 60 cm/sec. This cross section is usually best observed at a multiplane angle between 90 and 110 degrees and is ideal for assessing caval abnormalities, as well as compression of the right atrium from anteriorly located masses or effusions and the left atrium from posteriorly located masses or effusions. In addition, the bicaval cross section may reveal collections of air anteriorly located in the left or right atrium, as well as the structure of the interatrial septum including the foramen ovale. Often, rotating the transducer 10 to 15 degrees enhances the view of the tricuspid annulus. During this assessment, the image depth is decreased to 10 to 12 cm to afford a magnified view of the valves and color Doppler flow patterns. When air emboli collect in the left ventricle, they can usually be best observed in this view as very echogenic areas located along the anterior apical endocardial surface. However, the next and last of the basic cross sections provides a second look at the midventricular segments, as well as other benefits. To achieve this cross section, the transducer is rotated back to 0 degrees, the left ventricle is centered in the screen, and the probe is advanced 4 to 6 cm into the stomach. All major coronary arteries supplying the myocardium are viewed in this cross section. Twenty standard cross sections and their abbreviated names are depicted by the line drawings. The text describes the probe manipulations required to produce each of the cross sections. Because this cross section is used to judge filling and ejection, the image depth is consistently set to 12 cm to enable the size and function of the heart to be easily judged relative to previously examined hearts. The reason for this addition is the wealth of vital information this cross section can provide on the relative severity of atherosclerosis and the presence or absence of aortic dissection.
A subset of patients with symptoms of carcinoid syndrome excretes histamine at increased levels in their urine treatment for gout discount 5mg compazine overnight delivery. Histamine causes vasodilation of small blood vessels symptoms 6 days after iui compazine 5mg fast delivery, which leads to flushing and decreased total peripheral resistance. Histamine is known to cause bronchoconstriction, particularly in patients with bronchial asthma and other pulmonary diseases. Histamine receptor blocking drugs have been used with some success in alleviating the flushing associated with carcinoid syndrome. H2 antagonism alone was found to be just as effective as combination therapy in preventing symptoms; pure H1 antagonism, however, was ineffective. These therapies have been relegated to a second-line defense since the use of somatostatin. Catecholamines aggravate the symptoms of carcinoid syndrome, presumably by stimulating release of hormone by the tumor. Adrenergic receptors have not been demonstrated in carcinoid tumors, nor do these tumors usually have neural innervation. Perhaps adrenergic stimuli work through their mechanical effects on the gut and vessels to stimulate the release of tumor products. Treatment of patients with carcinoid tumors by means of - and -adrenergic antagonists has been beneficial in ameliorating flushing in some instances but ineffective in others. The results of prospective studies on somatostatin to ameliorate the symptoms of carcinoid syndrome have been dramatic. Somatostatin appears to be a major advance in the treatment of carcinoid syndrome. Bronchospasm with or without flushing also develops in many patients when vasoactive substances are released. Thus, a patient with carcinoid tumor may be well or may be severely incapacitated by pulmonary, neurologic, nutritional, fluid, electrolytic, or cardiovascular disturbances. What are the risks of giving anesthesia to patients with chronic impairment of liver function Although one may think that the experiences gained from providing anesthesia for liver transplantation would answer many of these questions, a substantial difference exists between optimizing cardiovascular function to meet the needs of a new liver. The sickle cell syndromes arise from a mutation in the -globin gene that changes the sixth amino acid from valine to glutamic acid. A major pathologic feature of sickle cell disease is the aggregation of irreversibly sickled cells in blood vessels. The molecular basis of sickling is the aggregation of deoxygenated hemoglobin B molecules along their longitudinal axis. Irreversibly sickled cells become dehydrated and rigid and can cause tissue infarcts by impeding blood flow and oxygen to tissues. Sickle cell trait is a heterozygous condition in which the individual has one S globin gene and one A globin gene, which results in the production of both hemoglobin S and hemoglobin A, with a predominance of hemoglobin A. Logic dictates that patients currently in crisis not undergo surgery except for extreme emergencies, and then only after an exchange transfusion. Meticulous attention to these practices in periods when we do not usually pay most careful attention. Even following these measures routinely, with no special emphasis placed on the periods described, succeeded in reducing mortality to 1% in several series of patients with sickle cell syndromes. Several investigators have advocated using partial exchange transfusions perioperatively. In children with sickle cell anemia and acute lung syndromes, partial exchange transfusion improved clinical symptoms and blood oxygenation. Clinical improvement of pneumococcal meningitis and cessation of hematuria in papillary necrosis also accompanied exchange transfusion. The 40% figure is an arbitrary one because no controlled studies have established a threshold ratio of hemoglobin A to hemoglobin S that would render blood unable to sickle in vivo. To achieve the 40% ratio in a 70-kg adult, approximately 4 units of washed erythrocytes would have to be exchanged; the system is inexpensive but efficient. The possible decrease in perioperative morbidity after partial exchange transfusion has not been compared with the risks of exchange, except in 2 studies,384,391 in which the risks of exchange were found to exceed the benefits. In the first study, a retrospective review of 82 surgical procedures performed between 1978 and 1986 in 60 patients, no advantage was noted for preoperative exchange transfusion as measured by a decrease in postoperative complications. More than 50% of the patients given transfusions had a postoperative complication. Patients who began with a hematocrit higher than 36% had a lower rate of complications.
Because ultrasonography is not a functional test per se symptoms genital herpes cheap compazine 5 mg without prescription, its use is not discussed further in this text medications hyponatremia discount compazine 5mg with amex. For example, events that reduce plasma flow rates reduce the hydraulic pressure of glomerular capillaries and favor decreased ultrafiltration, whereas events that increase plasma flow rate have the opposite effect. The glomerular filtration coefficient is the product of glomerular capillary hydraulic permeability and total surface area available for filtration. Hydrostatic pressures are normally maintained higher in glomerular capillaries than in other capillary beds by a delicate balance of preglomerular and postglomerular vascular tone in arterioles. The permeability of the glomerular capillary wall is equal for substances with molecular masses up to 5000 to 6000 daltons (Da) and decreases to almost zero at 60,000 to 70,000 Da. Serum creatinine is a cyclic anhydride of creatine, which is a small molecule (113 Da) that is continuously released during skeletal muscle protein catabolism. Muscle mass, which is smaller in women and declines with age, directly predicts creatinine release. These properties have made serum creatinine a mainstay as a marker of steady-state changes in renal filtration. Nonetheless, the serum creatinine concentration remains a useful; inexpensive; and, so far, unsurpassed clinical tool to reflect particularly trends of change in renal filtration function and to predict outcome, even during the perioperative period. Within the normal ranges, changes relative to baseline can represent significant changes in renal function. Thus a trend in serum creatinine values is always more useful than a single serum creatinine measurement to evaluate renal function reserve, particularly when changes are anticipated. In addition, creatinine generation rates may change under conditions of acute illness. Creatinine clearance can be either estimated when creatinine is at steady state or directly measured. The major limitation in determining creatinine clearance is the necessity of accurately collecting urine. However, changing hydration of the patient and failing to record urine volume accurately may make such short-timed collections inaccurate. These individuals include older and critically ill patients who may have limited muscle mass, as well as those who are under conditions of acute stress and critical illness, during which emerging data have suggested that changes in creatinine generation may occur. However, two important caveats must be kept in mind when interpreting these results. Urine Volume Although consistently recorded, intraoperative urine output remains a controversial perioperative marker of renal function. Whereas the presence of urine (regardless of amount) confirms blood flow to the kidney, many nonrenal factors directly and profoundly influence urine production. During surgery, patients are often hemodynamically unstable; decreased blood volume or cardiac output, fluctuating hormone levels. In settings of poor perfusion or prerenal azotemia, urine specific gravity is high. Of note, the ability of the kidneys to concentrate urine is impaired in many older patients and many with chronic kidney disease. Urine specific gravity is a surrogate for osmolality (normal range, 50 to 1000 mOsm/kg), a measure of the number of osmotically active particles in solution in the solvent phase. Theoretically, urine osmolality is physiologically superior to urine specific gravity as a test of renal function; however, the same substances and conditions that render urine specific gravity a nonspecific test can also affect the reliability of urine osmolality (see Box 52-2). Urinary Sodium Concentration With decreasing perfusion, the normally functioning kidney conserves sodium and water. Consequently, rigorous attempts to distinguish one disease from the other have been unsuccessful; perhaps, as a result, this distinction should not be made. The FeNa was first described by Espinel158; it represents the fraction of sodium excreted versus that filtered by the kidneys. Some have proposed that the fractional excretion of urea can be useful in this context, with a fractional excretion of urea of <35% being consistent with prerenal azotemia, even in the setting of diuretic use.