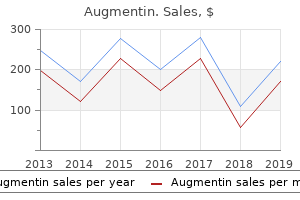
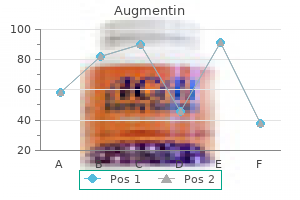
Augmentin
"Order augmentin 375mg without a prescription, virus martin garrix".
By: X. Aschnu, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of New Mexico School of Medicine
But if the lens is pulling on the iris virus types generic 625 mg augmentin amex, use a Sinskey hook (or some other type of anterior segment instnlment of your choice) to push and pull the lens at the haptic-optic junctions antibiotics kill bacteria 625mg augmentin for sale. Pull in toward the center of the pupil and walk the lens circumferentially around until you are happy with the po1ition. Many surgeons do thill on every 128 Chapter 7 case in order to move the haptics away from the large wound, but this is unnecessary in many cases. Once you are happy with the lens position, sew the corneal or scleral wound, and you are done. Once you understand the basics, you can learn any one of these techniques by watching a few videos. Alternately, you can use 3 and make 2 other incisions with trocar blades without placing cannulas in those incisions. If you do it this way, you will have an infusion, 2 superior cannulas, and 2 inferior trocar blade incisions. Regardless, we have found it helpful to move our seated position superiotemporally rather than straight superiorly in these cases. The 4 other incisions are then placed 3 mm from the limbus, centered 2 mm on either side of an imaginary line running through the middle of the pupil from inferiotemporal to superionasal. The 2 more inferior trocars (or incisions) will be used (along with the superior trocars) to thread the GoreTex sutures through the sclera. We find it helpful to use a toric marker to make marks on both sides of the limbus along this Approach to lntraocular Lens Cases 129 imaginary line. Calipers can be used to measure 2 mm on either side of the marks and 3 mm back from the limbus. Careful attention to these measurements will allow accurate placement of the trocars and, later, perfect centering of the lens. When you are ready to place the lens, make a corneal incision with a keratome blade about 4 mm in width (bigger is easier but may require an extra stitch). Use 1 piece of Gore-Tex to thread through 2 of the eyelets on 1 side of the lens, and use another piece to thread through the eyelets on the other side. Do the inferior side first (the Gore-Tex suture coming out of the more inferior eyelet goes to the more inferior trocar), then the superior (the Gore-Tex suture coming out of the more superior eyelet goes to the more superior trocar). Four additional trocars have been placed 3 mm from the llmbus and 2 mm from the mldllne. The Gore-Tex suture Is passed through tfte corneal Incision and handed to a pair of Max. Nate: this eye Is quite bloody beause this was a patlentwltft a history of an open globe and scarred conjunctiva. Then, place the superior Gore-Tei suture through the corneal wound well away from the inferior stitch so it i& impossible to tangle. Early on in our experience with the1e leD5es, we found threading the nasal side to be a chore because of the brow. Placing the trocars as we have described previously takes the brow out of the equation and makes this step much easier. The bent forceps allow us to sit per usual superiorly without shifting trocar placement and manage the nasal sutures without much difficulty. The Gore-Tex suture hH been th~aded through the comet incision and out of all 4 trocars. After you have threaded each of the ends of the Gore-Tex sutures through the cornea and out of the trocau, insert the lens. The troars h1111e bffn removed, and the suturff are tied in 1 3-1-1 fashion to ensure perfect centerlng. Not placing cannulu in the inferior sclerotomies (u mentioned earlier) and then burying the knots in the superior sclerotomies may allo help lower the risk of hypotony.
Diseases
- Trisomy 1 mosaicism
- Worster-Drought syndrome
- Female pseudohermaphrodism Genuardi type
- Genito palatocardiac syndrome
- Anophthalia pulmonary hypoplasia
- Lung herniation congenital defect of sternem
- Maroteaux Lamy syndrome
- Bradykinesia
The committee of experts concluded that improving the quality and availability of medical and social services for patients and their families could not only enhance the quality of life through the end of life but may also contribute to a more sustainable care system antibiotics xerostomia purchase augmentin 625mg with mastercard. A comparative antibiotic resistance video order generic augmentin from india, retrospective, observational study of the prevalence, availability, and specificity of advance care plans in a county that implemented an advance care planning microsystem. This paper looks at the outcomes of a managed, systematic approach to advance care planning over time. The authors proved that it is possible to achieve a high prevalence of advance care plans that are specific enough to assist with clinical decisions. Creating such a system requires a sustained commitment of resources and leadership that results in a health care culture in which knowing and honoring patient preferences is a high priority. The author provides a personal perspective on age-related frailty, serious illness, and approaching death as he follows his father and grandmother-in-law through their own end-of-life journeys. He compares and contrasts the Western medical reality with more traditional societies as he explores aging and dying. The book emphasizes the need for better communication between patients, families, and their caregivers at the end of life. They found that early palliative care led to significant improvements in both quality of life and mood. They also found that when compared to patients receiving standard care, patients receiving early palliative care had less aggressive care at the end of life but longer survival. Best case/worst case: Training surgeons to use a novel communication tool for high-risk acute surgical problems. This group of authors developed a communication tool, "Best Case/Worst Case," that is based on an established conceptual model of shared decision making that helps facilitate difficult decision making. This paper showed that surgeons trained in its use found it to help establish patient expectations, provide clarity, and facilitate deliberation. They showed that structured communication between physicians and families resulted in earlier consensus around goals of care for dying trauma patients. Since specialist palliative care is delivered by an interdisciplinary team and not all trauma centers may have the luxury of having a boardcertified palliative care provider, these guidelines provide a framework for incorporating the most essential aspects of palliative care into the trauma setting. The authors review important aspects of end-of-life care, including how to discuss goals of care, or running a family care conference. Background Communication between surgeons, patients, and surrogates about goals of treatment plays an important and understudied role in determining the surgical interventions elderly patients with serious illness receive. Communication breakdowns may lead to nonbeneficial procedures in acute events near the end of life. Methods We review the available literature on factors that lead to communication challenges and nonbeneficial surgery at the end of life. We use this review to identify solutions for navigating surgical decision making for seriously ill elderly patients with acute surgical conditions. Results Surgeon, patient, surrogate, and systemic factors-including time constraints, inadequate provider communication skills and training, uncertainty about prognosis, patient and surrogate anxiety and fear of inaction, and limitations in advance care planning-contribute to communication challenges and nonbeneficial surgery at the end of life. Conclusions Improved communication among surgeons, patients, and surrogates is necessary to ensure that patients receive the care that they want and to avoid nonbeneficial treatment. Further research is needed to learn how to best structure these conversations in the emergency surgical setting. Original Author Commentary: Zara Cooper Although potentially lifesaving, major surgery in frail and seriously ill patients may worsen functional disability and exacerbate chronic symptoms, leading to institutionalization and worse quality of life. The benefits of surgery must be weighed against the uncertainty of other poor outcomes that may be unacceptable to patients. The evidence about longer-term patient outcomes to inform clinical decisions is sparse and decisions are marked by emotional distress on the part of patients, family members, and clinicians alike. As we describe in this article, the epicenter of each decision is a conversation between surgeons and patients or surrogates that is heavily influenced by factors that are frequently out of the control of either party. However, too frequently, clinical momentum and inadequate communication leads to patients receiving surgery that cannot achieve their clinical goals. Surgeons must also embrace palliative adjuncts or alternatives to surgery that can alleviate suffering and help patients better reach their goals near the end of life. Vercruysse 50 Alcohol in various forms has been made, traded, sold and used by humans for millennia. Beer and wine were noted to be safe alternatives to the relatively unsafe sources of available polluted water found in most cities during the middle ages and was and still is produced by monks for personal use and trade.
Socioeconomic status and the brain: Mechanistic insights from human and animal research virus 79 buy cheap augmentin. Socioeconomic status is positively correlated with frontal white matter integrity in aging virus update flash player purchase augmentin 375 mg mastercard. Socioeconomic disadvantage, neural responses to infant emotions, and emotional availability among first- time new mothers. How socioeconomic disadvantages get under the skin and into the brain to influence health development across the lifespan. A metaanalysis of the relationship between socioeconomic status and executive function per for mance among children. Strengths and weaknesses of neuroscientific investigations of childhood poverty: Future directions. The effects of poverty on childhood brain development: the mediating effect of caregiving and stressful life events. Central role of the brain in stress and adaptation: Links to socioeconomic status, health, and disease. Socioecomomic status, amygdala volume and internalizing symptoms in children and adolescents. Socioeconomic inequality and the developing brain: Spotlight on language and executive function. Neural mechanisms linking social status and inflammatory responses to social stress. Family-based training program improves brain function, cognition, and behav ior in lower socioeconomic status preschoolers. Family income, parental education and brain structure in children and adolescents. Brain-behavior relationships in reading acquisition are modulated by socioeconomic factors. Early-life adversity and physical and emotional health across the lifespan: A neuroimmune network hypothesis. Proficiency differences in syntactic processing of monolingual native speakers indexed by event-related potentials. Brain imaging and electrophysiology biomarkers: Is there a role in poverty and education outcome research Socioeconomic status and reading disability: Neuroanatomy and plasticity in response to intervention. Science does not speak for itself: Translating child development research for the public and its policymakers. The impact of socioeconomic status on the neural substrates associated with plea sure. Socioeconomic status and academic achievement: A meta- analytic review of research. An epigenetic mechanism links socioeconomic status to changes in depression-related brain function in high-risk adolescents. Neurocognitive development in socioeconomic context: Multiple mechanisms and implications for mea sur ing socioeconomic status. A mechanistic understanding of addiction is thus crucial for addressing these public health issues. To date, addiction research has made tremendous progress in terms of uncovering the neurobiological and neuropsychological correlates of addiction. However, little is known about the computational principles implemented by the brain. This explanatory gap hinders the understanding of the mechanisms of addiction as well as the development of effective therapeutics. In this article we will review recent efforts in the nascent field of computational psychiatry that have started to address this problem. Second, we will review studies utilizing theory- driven computational approaches, including reinforcement-learning models, Bayesian models, and biophysical models, that address addiction. Last, we will outline a road map for computational work on addiction to move forward.
Vaccinium Angustifolium (Blueberry). Augmentin.
- Preventing cataracts and glaucoma, ulcers, urinary tract infections (UTIs), multiple sclerosis (MS), chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), fever, sore throat, varicose veins, hemorrhoids, bad circulation, diarrhea, constipation, labor pains, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Blueberry?
- How does Blueberry work?
- Dosing considerations for Blueberry.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96974