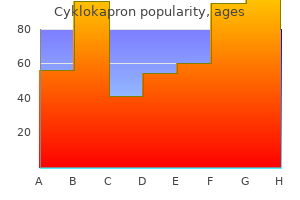
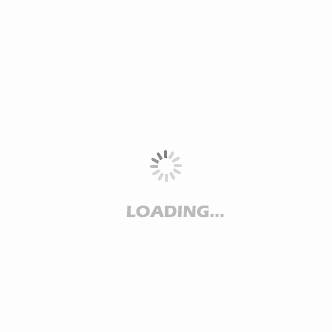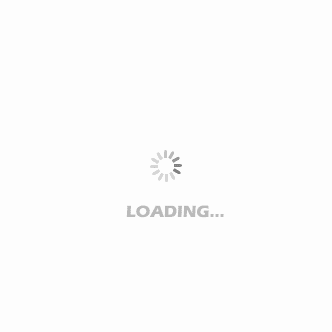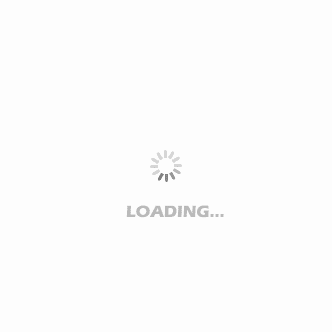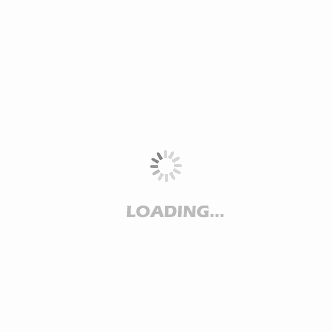
Cyklokapron
"Generic cyklokapron 500mg on line, jnc 8 medications".
By: W. Hernando, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Clinical Director, University of California, Davis School of Medicine
The expectation is that the associated skills are achieved before training on patients commences medications ending in zole cyklokapron 500 mg overnight delivery. Once competent treatment warts generic cyklokapron 500mg amex, the trainee is expected to continue to perform procedures and keep a log recording any with complications and how these were resolved [46]. They consist of Capabilities in Practice (CiPs) with defined specific key skills and procedures and the levels that trainees should have reached by the end of their training. The changes reflect the generic professional capabilities required by the General Medical Council [47]. As part of the training programme, trainees are expected to attend an intermediate- to advanced-level hysteroscopic surgery course, where practice on simulation models is provided. The practical aspects of the course focus on hysteroscopic skills, but this also includes the ability to insert contraceptive and therapeutic intrauterine devices. The course is delivered as a combination of short residential modules with lectures and practical skills workshops, and work-based training under supervision of a consultant gynaecologist with expertise in hysteroscopy. Typically, the course is completed 232 18: Training in Hysteroscopic Skills within 18 months. More recently, a similar course commenced for general practitioners with a special interest in gynaecology. Individual differences in skill learning: an integration of psychometric and information processing perspectives. Deliberate practice and the acquisition and maintenance of expert performance in medicine and related domains. Spatial ability and learning the use of an angled laparoscope in a virtual environment. Instructor feedback versus no instructor feedback on performance in a laparoscopic virtual reality simulator: a randomized educational trial. Instructor feedback versus no instructor feedback on performance in a laparoscopic virtual reality simulator: a randomized trial. Proficiency maintenance: impact of ongoing simulator training on laparoscopic skill retention. Twelve tips for developing and implementing an effective surgical simulation programme. Implementation of the laparoscopic simulator in a gynaecological residency curriculum. Implementation of simulation in surgical practice: minimally invasive surgery has taken the lead: the Dutch experience. Proving the effectiveness of virtual reality simulation for training in laparoscopic surgery. Aspiring to Excellence: Findings and Final Recommendations of the Independent Inquiry into Modernising Medical Careers. Improving continuing medical education for surgical techniques: applying the lessons learned in the first decade of minimal access surgery. Defining a structured training program for acquiring basic and advanced laparoscopic psychomotor skills in a simulator. Fundamental principles of validation and reliability: rigorous science for the assessment of surgical education and training. Establishing construct validity of a virtual-reality training simulator for hysteroscopy via a multimetric scoring system. Hysteroscopic placement of tubal sterilization implants: virtual reality simulator training. A virtual reality simulator for hysteroscopic placement of tubal sterilization micro-inserts: the face and construct validity. Hysteroscopic sterilization using a virtual reality simulator: assessment of learning curve. Justin Clark One of the fundamental maxims of surgery is to work with excellent visualisation of the operative field. The advent of hysteroscopy, endoscopic visualisation within the uterus, has threatened the existence of blind intrauterine procedures. Technological advances, particularly in optics and ancillary equipment, have led to hysteroscopic surgery becoming increasingly adopted.
The genetic analysis of a switch-regulation pathway is based on the phenotypes of double mutants of pairs of genes in which the mutant alleles show contrasting phenotypes symptoms wheat allergy generic cyklokapron 500 mg fast delivery. The order of the components in the switch-regulation pathway is determined by the type of epistasis observed in the double mutants medications not to take after gastric bypass purchase cyklokapron overnight. A classical definition of epistasis is any interaction between mutant alleles that alters the 9: 3: 3: 1 ratio expected from independent assortment of two genes. In the analysis of switch-regulation pathways the term is used in a somewhat different sense. For double mutants with alleles in genes with contrasting phenotypes, a gene is called an epistatic gene if its mutant phenotype masks the mutant phenotype of another gene. For example, if the phenotype of aa bb is the same as that of aa b1b1, then the gene a is said to be epistatic to the gene b. The gene whose mutant phenotype is concealed is called a hypostatic gene, and in the previous example the b gene is hypostatic to the a gene. Equivalently, we could say that the multivulva gene is hypostatic to the vulvaless gene. Epistasis helps to determine the order of components in a developmental pathway for the following reason: Principle of epistasis: In a linear switch-regulation pathway, the product of the epistatic gene acts downstream in the pathway relative to the product of the hypostatic gene; to say the same thing in another way, the product of the hypostatic gene acts upstream relative to that of the epistatic gene. The phenotype of a2 b2 is the same as that of a1 b2; hence b is epistatic to a, and so B acts downstream of A. The gene product of the epistatic gene acts downstream of the product of the hypostatic gene. Two switch-regulation pathways are shown in which mutants yield opposite phenotypes, either vulvaless or multivulva. In both pathways, A and B represent the wildtype gene products of the genes a and b, respectively. By convention, the arrowhead implies positive regulation (stimulation) and the T-bar implies negative regulation (inhibition). If there are intervening components, then the arrows and bars represent the net effect on the intervening components. The a2a2 b1b1 genotype therefore has less inhibition of B, and the resulting greater activity of B implies a phenotype of multivulva. In contrast, the a1a1 b2b2 genotype lacks B and hence no vulva induction occurs, yielding a phenotype of vulvaless. Pathway 2 has the order of A and B interchanged, and, in this case, the a2a2 b1b1 phenotype is vulvaless and that of a1a1 b2b2 is multivulva. In pathway 1 the a2a2 b2b2 double mutant is vulvaless because the animal lacks B, whereas in pathway 2 the a2a2 b2b2 double mutant is vulvaless because the animal lacks A. In both cases, in accord with the principle of epistasis, the gene that is downstream in the pathway is epistatic to the gene that is upstream in the pathway. The phenotypes of the mutants are shown color coded, brown for vulvaless and green for multivulva. To define the switch-regulation pathway based on epistasis, a researcher would examine the phenotype of each of the double mutants shown in the square, which are also color coded. The principle of epistasis says that the phenotype of the (A) double mutant is the same as that of the single mutant whose product acts farEach double mutant is either ther downstream. The pathway symbols are dashes instead of arrows (stimulalet-23 - let-60 - lin-45 the phenotype of the tion) and T-bars (inhibition). The reason double mutant is that is that the linear order of components of the single mutant let-23 - lin-1 in the pathway should be deduced first. A strategy for doing this is to start with the last component in the pathway and work backwards. The reasoning is based on the nature of each type of mutant (loss of function or gain In the linear switch-regulation pathway illustrated of function). For example, lin-1 is a loss of function below, X and Y are gene products, the arrow denotes allele that results in a multivulva phenotype. Since positive regulation, and the T-bar denotes negative loss of lin-1 activity promotes vulva formation, the wildtype activity of the Lin-1 protein must be inhibregulation (inhibition).
The observations made in these nine cases (five boys and four girls) are recorded in the [accompanying] table medications you can buy in mexico purchase cyklokapron 500 mg with amex. It therefore seems legitimate to conclude that there exists in Down syndrome children a small supernumerary telocentric chromosome symptoms depression discount 500mg cyklokapron otc, accounting for the abnormal figure of 47. To explain these observations, the (continued) hypothesis of nondisjunction of a pair of small telocentric chromosomes at the time of meiosis can be considered. It is, however, not possible to say that the supernumerary small telocentric chromosome is indeed a normal chromosome and at the present time the possibility cannot be discarded that a fragment resulting from another type of aberration is involved. These results were persuasive, but they also pointed to the uncertainty involved in karyotype analysis-in some cases, the karyotypes of individual cells may be difficult or impossible to accurately determine. It is for this reason that, in modern diagnostic tests of embryonic cells, the karyotypes of multiple cells (typically 20) are usually determined. When significant effects have been found, they are usually small and not always reproducible, due in part to confounding effects of other factors such as maternal age. In view of the maternal-age effect, the female sex hormone estrogen and molecules resembling estrogen have long been under suspicion. With this background in mind, it was no great surprise to learn that modest concentrations of a common estrogen mimic known as bisphenol A [technical name 2,2-(4,4-dihydroxy-diphenol) propane] caused about an eightfold increase in the incidence of aneuploidy in mice. Bisphenol A is the basic subunit of polycarbonate plastic products widely used as a can liner in the food and beverage industry. In its polymerized form it may be completely harmless, but the monomers can leach out of plastic products under certain conditions. It is noteworthy that detectable levels of the chemical are found in the urine of 90 percent of the U. Chromosome aberrations were initially discovered through their genetic effects, which, though confusing at first, were eventually understood as resulting from abnormal chromosome structure. Deletions are generally harmful to the organism, and the usual rule is the larger the deletion, the greater the harm. Very large deletions are usually lethal, even when heterozygous with a normal chromosome. Small deletions are often viable when they are heterozygous with a structurally normal homolog, because the normal homolog supplies gene products that are necessary for survival. However, even small deletions are usually homozygous-lethal (when both members of a pair of homologous chromosomes carry the deletion). Chromosome breaks occur spontaneously at a low rate, but they can also be induced by x-rays and certain 5. Each of the principal types of structural aberrations has characteristic genetic effects. To centromere Yellow gradients depict position and orientation of inverted repeats containing a set of fertility genes. Ectopic recombination within red region results in loss of both copies of the fertility genes. B Ectopic recombination within blue region results in loss of one copy of the fertility genes. A deletion is created when a chromosome arm is broken in two places, when the broken ends bearing the centromere and the telomere fuse and the part left out remains as an acentric fragment that is lost. If the direct repeats undergo pairing and homologous recombination, the result is a deletion of the material between the direct repeats, because the small circular acentric fragment containing this material is lost. The red and blue gradients indicate direct repeats, whereas the yellow gradients indicate inverted repeats, in which the repeated sequences are in reverse orientation. To give an idea of scale, the red repeats are each 229 kb in length, and the region between the repeats is 3. As shown in the diagram, homologous recombination in the red repeats results in loss of both sets of copies of the male-fertility genes. A deletion with less drastic effects results from recombination within the blue repeats, which yields a deletion of only one set of the fertility genes. Although loss of these genes does not result in complete sterility, it does impair spermatogenesis. Deletions can be detected genetically by making use of the fact that a chromosome with a deletion no longer carries the wildtype alleles of the genes that have been eliminated. For example, in Drosophila, many Notch deletions are large enough to remove the nearby wildtype allele of white also. When these deleted chromosomes are heterozygous with a structurally normal chromosome carrying the recessive w allele, the fly has white eyes because the wildtype w+ allele is no longer present in the deleted Notch chromosome.