Retrovir
"Purchase retrovir on line, treatment of diabetes".
By: H. Tukash, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Kaiser Permanente School of Medicine
In healthy adults treatment high blood pressure 100 mg retrovir free shipping, one drop of solution in both eyes 4 times daily for 7 days produced a peak plasma concentration of 7 medicine effects purchase retrovir toronto. The elimination half-life apparently has not been determined, but plasma levels were below the quantifiable limit (2 ng/mL) at 24 hours. When this higher dose was given during the perinatal and lactation periods, an increase in stillbirths and decreased growth and development were observed in rat pups. In rabbits during organogenesis and fetal development, doses >13,000 times the human dose based on body weight were not teratogenic (1). Bepotastine did not significantly induce neoplasms in mice or rats in longterm studies. The molecular weight (about 389 for free acid) and moderate plasma protein binding suggest that the drug will cross to the embryofetus. However, the minimal systemic bioavailability suggests that the exposure will be clinically insignificant. The molecular weight (about 389 for free acid) and moderate plasma protein binding suggest that the drug will be excreted into breast milk. However, the minimal systemic bioavailability suggests that any exposure of a nursing infant will be clinically insignificant. Because the systemic bioavailability of the antibiotic is very low, the risk to the embryo or fetus also appears to be low. Besifloxacin is in the same subclass of ophthalmic antibiotics as ciprofloxacin, gatifloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, norfloxacin, and ofloxacin. Maximum plasma concentrations after bilateral dosing 3 times daily for 16 doses were <1. Increased postimplantation loss, decreased fetal weights, and decreased fetal ossification were noted, but these doses also produced maternal toxicity (reduced body weight gain and food consumption) and mortality. The drug was not mutagenic in one test but, similar to other quinolones, was mutagenic in another test. No impairment of fertility in male and female rats was observed with oral doses that were >10,000 times the daily human ophthalmic dose (1). The molecular weight (about 394 for the free base) and long plasma elimination half-life suggest that the drug will cross to the embryofetus. However, the minimal plasma concentrations suggest that the exposure will not be clinically significant. The molecular weight (about 394 for the free base) and long plasma elimination half-life (7 hours) suggest the drug will be excreted into breast milk. Even with therapeutic doses of the drug, serum levels of vitamin A do not rise above normal. Studies in animals have failed to show a teratogenic effect (see also Vitamin A) (2). A single case describing the therapeutic use of this vitamin in human pregnancy has been located. Serum levels of -carotene and retinol (vitamin A) were determined 2 weeks after her last dose. She delivered a healthy, normal-appearing, 3910-g male infant without skin discoloration at term. Clinical teratology counseling and consultation report: high dose -carotene use during early pregnancy. Betamethasone was not specifically identified in these studies, but only one study listed the corticosteroids used (see Hydrocortisone for details). The drug is partially metabolized (47%) by the perfused placenta to its inactive 11-ketosteroid derivative but less so than other corticosteroids, although the differences are not statistically significant (17). In addition, moderate to severe respiratory morbidity was increased over that in controls, 21. Slower lung maturation in male fetuses has been cited as a major contributing factor to the sex differential noted in neonatal mortality (28). Therapy is also less effective in multiple pregnancies (27,29), even when doses have been doubled (27). In twins, only the first-born seems to benefit from antenatal steroid therapy (27). An increased incidence of hypoglycemia in newborns exposed in utero to betamethasone has been reported (30). Although other investigators have not observed this effect, maternal betamethasone-induced hyperglycemia is a possible explanation if the drug was given shortly before delivery.
Fetal breathing movements increased significantly during the 3rd hour after regular coffee medications parkinsons disease discount retrovir 300 mg, rising from 144 breaths/hour to 614 breaths/hour (p <0 medications narcolepsy buy discount retrovir. However, the mean number, amplitude, and duration of fetal heart rate accelerations did not differ statistically from the control period. Decaffeinated coffee also caused a significant increase in fetal breathing movements, rising to 505 breaths/hour during the 2nd hour, but this beverage caused only a slight, nonsignificant lowering of the fetal heart rate. In an earlier study using 200-mg tablets of caffeine, no increase in fetal breathing rates was observed (32). The differences between the two studies may have been related to the lower dose and/or the dosage form of caffeine. Cardiac arrhythmias and other symptoms in newborn infants were associated with maternal caffeine consumption of >500 mg/day (N =16) in comparison with the offspring of women who used less than 250 mg/day (N = 56) of caffeine (33). The percentages of observed symptoms in the infants of the high and low caffeine groups were tachyarrhythmias (supraventricular tachycardia and atrial flutter) 25% vs. Two reports have described adverse fetal outcomes, including teratogenic effects, in the offspring of two mothers taking migraine preparations consisting of ergotamine and caffeine (34,35). A 1993 reference compared the effects of maternal caffeine consumption greater than 500 mg/day with those of less than 200 mg/day on fetal behavior in the 3rd trimester (36). Fetuses of mothers in the high caffeine group spent less mean time in active sleep, similar mean time in quiet sleep, and much greater mean time in arousal than did low caffeine-exposed fetuses. It could not be determined if the modulation of behavior had any clinical significance to the newborn or in later life (36). A 2001 review concluded that, in those who do not smoke or drink alcohol, moderate caffeine consumption (<56 mg/kg/day spread throughout the day) did not increase any reproductive risks (37). However, confirmation of these findings is needed before any firm conclusions can be drawn. The consumption of high caffeine doses with cigarette smoking may increase the risk for delivery of infants with lower birth weight than that induced by smoking alone. Moreover, consumption of large amounts of caffeine may be associated with becoming a smoker and excessive alcohol drinking (37). Following ingestion of coffee or tea containing known amounts of caffeine (36335 mg), peak milk levels of 2. In this and an earlier study, the authors estimated a nursing infant would receive 1. Nine breastfeeding mothers consumed a measured amount of caffeine (750 mg/day) added to decaffeinated coffee for 5 days, then abstained from all caffeine ingestion for the next 4 days (44). In six women, 24-hour pooled aliquots of milk samples from each feeding were collected on days 5 and 9. The average milk caffeine concentrations from these seven mothers on day 5 were 4. On day 9, caffeine was detectable in the sera of only two infants, decreasing from 0. The remaining two mothers collected milk samples with each feeding for the entire 9 days of the study but did not pool the samples. These mothers were breastfeeding infants aged 79 and 127 days, and their mean daily milk caffeine levels on days 15 ranged from 4. In an extension of the above study, the effect of 500 mg of caffeine consumption/day on infant heart rate and sleep time was evaluated in 11 motherinfant pairs (45). Mothers consumed decaffeinated coffee daily for 5 days and then decaffeinated coffee with added caffeine for another 5-day period. No significant difference in 24-hour heart rate or sleep time was observed between the two phases of the study. The elimination half-life of caffeine is approximately 80 hours in term newborns and 97. A 1987 study investigated the metabolism of caffeine in breast- and formula-fed infants given oral doses of caffeine citrate (46). The serum half-lives of caffeine were greater than three times as long in the breast-fed infants as compared with the formula-fed infants (76 vs.
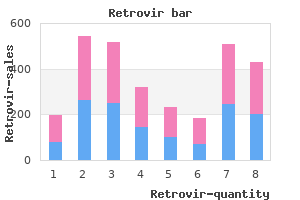
The findings included delayed ossifications and skeletal variations at doses that were about 0 medicine nausea purchase retrovir with visa. Studies evaluating the carcinogenic potential of cabozantinib have not been conducted medicine advertisements order retrovir with american express. Fertility was impaired in male rats (decrease in sperm counts and reproductive organ weights) and female rats (decrease in live embryos and increase in pre- and postimplantation losses, and ovarian necrosis). Impairment of fertility also was observed in male (hypospermia) and female (absence of corpora lutea) dogs (1). The molecular weight (about 636 for the malate salt) and the long effective half-life suggest that the drug will cross to the embryofetus, but the high plasma protein binding might limit the exposure. The molecular weight (about 636 for the malate salt) and the long effective half-life (about 55 hours) suggest that the drug will be excreted into breast milk, but the high plasma protein binding (99. However, because the drug commonly (25%) causes toxicity in adults, such as diarrhea, stomatitis, decreased appetite and weight, nausea, fatigue, and oral and abdominal pain, the best course is to not use cabozantinib during breastfeeding. It is frequently used in combination products containing aspirin, phenacetin, and codeine and is present in a number of commonly consumed beverages, such as coffee, teas, and colas, as well as many food items. The mean caffeine content in the usual servings of some common beverages was reported as caffeinated coffee (66 146 mg), nonherbal tea (2046 mg), and caffeinated soft drinks (47 mg) (2), but these amounts may vary widely. The mutagenicity and carcinogenicity of caffeine have been evaluated in more than 50 studies involving laboratory animals, human and animal cell tissue cultures, and human lymphocytes in vivo (1,3). The significance of mutagenic and carcinogenic effects found in nonmammalian systems has not been established in man. The drug is an animal teratogen only when doses high enough to cause toxicity in the mother have been given (1). In this group, slightly increased relative risks were found for musculoskeletal defects, hydronephrosis, adrenal anomalies, and hemangiomas or granulomas, but the results are not interpretable without independent confirmation (7, pp. Other reports have also found no association between the use of caffeine during pregnancy and congenital malformations (912). However, a few of these studies have isolated the effects of caffeine from cigarette or alcohol use, both of which are positively associated with caffeine consumption (3). One German study has observed that high coffee use alone is associated with low birth weights (18). In an American study of more than 12,400 women, low birth weights and short gestations occurred more often among offspring of women who drank four or more cups of coffee/day and who smoked (12). No relationship between low birth weights or short gestation and caffeine was found after controlling for smoking, alcohol intake, and demographic characteristics. However, other investigators have questioned whether this study has accurately assessed the total caffeine intake of the women (19,20). A Canadian study retrospectively investigated 913 newborn infants for the effects of caffeine and cigarette smoking on birth weight and placental weight (21). Significant caffeine cigarette interactions were found when daily consumption of caffeine was 300 mg. Compared with nonsmokers, cigarette smoking significantly lowered mean birth weight. When caffeine use was considered, daily consumption of 300 mg combined with smoking 15 cigarettes caused an additional significant reduction in weight. Head circumference and body length were not affected by any level of caffeine consumption. Placental weight, which normally increases with cigarette smoking, an effect hypothesized to be due to compensatory hypertrophy induced by chronic fetal hypoxia, was found to decrease significantly in women smoking 15 cigarettes/day and ingesting 300 mg of caffeine/day (21). Caffeine consumption was calculated based on the intake of coffee (107 mg/serving), tea (34 mg/serving), colas (47 mg/serving), and drugs. The data were adjusted for factors such as demographic characteristics, obstetric and medical histories, contraceptive use, smoking, and alcohol exposure. The mean 1st trimester caffeine consumption was statistically similar in those who aborted compared with those who delivered liveborn infants, 125. After adjustment for other risk factors, notably smoking, the adjusted odds ratios for growth restriction and microcephaly were 1.
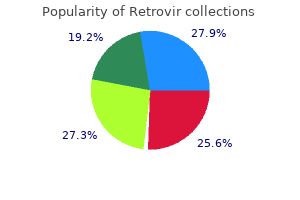
Successful delivery following continuous cytostatic therapy of a leukemic pregnant woman medications while pregnant 100 mg retrovir amex. Pregnancy after treatment with hydroxyurea in a patient with primary thrombocythaemia and a history of recurrent abortion treatment 32 discount 100 mg retrovir with amex. Successful outcome of pregnancy in a case of essential thrombocytosis treated with hydroxyurea. Hydroxyurea use during pregnancy: a case report in sickle cell disease and review of the literature. Exposure to hydroxyurea and pregnancy outcomes in patients with sickle cell anemia. Exposure to , hydroxyurea during pregnancy in sickle-Я thalassemia: a report of a case. Influence of chemotherapy for gestational trophoblastic disease on subsequent pregnancy outcome. Polycythemia vera and pregnancy: a case report with the use of hydroxyurea in the first trimester. Although a surveillance study found an increased risk of oral clefts, this defect has not been observed in other studies. The drug is teratogenic in mice and rats, but not in rabbits, at high doses (15). One report suggested that hydroxyzine teratogenicity was mediated by a metabolite (norchlorcyclizine) that was common to four antihistamines (hydroxyzine, buclizine, meclizine, and chlorcyclizine) (3). Highdose hydroxyzine (612 mg/kg/day) resulted in abortions in rhesus monkeys (6). The manufacturer considers hydroxyzine to be contraindicated in early pregnancy because of the lack of clinical data (1,2). The molecular weight of the free base (about 376) suggests that the drug will cross to the embryo and fetus. In 100 patients treated in the 1st trimester with oral hydroxyzine (50 mg daily) for nausea and vomiting, no significant difference from nontreated controls was found in fetal wastage or anomalies (7). A woman treated with 60 mg/day of hydroxyzine during the 3rd trimester gave birth to a normal infant (8). The Collaborative Perinatal Project monitored 50,282 motherchild pairs, 50 of whom had 1st trimester exposure to hydroxyzine (9, pp. Based on five malformed children, a possible relationship was found between 1st trimester use and congenital defects. In a surveillance study of Michigan Medicaid recipients involving 229,101 completed pregnancies conducted between 1985 and 1992, 828 newborns had been exposed to hydroxyzine during the 1st trimester (F. Specific data were available for six defect categories, including (observed/expected) 9/8 cardiovascular defects, 1/0. Withdrawal in a newborn exposed to hydroxyzine 600 mg/day throughout gestation has been reported (10). The mother, who was being treated for severe eczema and asthma, was also treated with phenobarbital, 240 mg/day for 4 days and then 60 mg/day, for mild preeclampsia during the 3-week period before delivery. Symptoms in the newborn, some beginning 15 minutes after birth, consisted of a shrill cry, jitteriness with clonic movements of the upper extremities, irritability, and poor feeding. The presumed drug-induced withdrawal persisted for approximately 4 weeks and finally resolved completely after 2 weeks of therapy with phenobarbital and methscopolamine. Although phenobarbital withdrawal could not be excluded, and neonatal withdrawal is a well-known complication of phenobarbital pregnancy use, the author concluded the symptoms in the infant were primarily caused by hydroxyzine (10). A 1996 report described the use of hydroxyzine, droperidol, diphenhydramine, and metoclopramide in 80 women with hyperemesis gravidarum (11). All women received approximately 200 mg/day of hydroxyzine in divided dosage for up to a week after discharge from the hospital, and 12 (15%) required a second course of therapy for recurrence of their symptoms. Only the latter anomaly is a potential drug effect, but the most likely cause was thought to be the result of an in utero fetal vascular accident or infection (11). A 2001 study, using a treatment method similar to the above study, described the use of droperidol and diphenhydramine in 28 women hospitalized for hyperemesis gravidarum (12). The study group appeared to have more severe disease than controls as suggested by a greater mean loss from the prepregnancy weight, 2. In controls, there was one major malformation of unknown cause, an acardiac fetus in a set of triplets, and one newborn with a genetic defect (Turner syndrome).